Demystifying the Process: A Comprehensive Guide to Install Linux
Installing Linux: A Step-by-Step Guide
Linux, the open-source operating system, has gained immense popularity over the years due to its flexibility, security, and vast range of available software. If you’re ready to take the plunge and install Linux on your computer, this step-by-step guide will help you navigate through the installation process smoothly.
Choose a Linux Distribution:
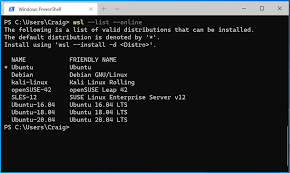
The first step is to select a Linux distribution that suits your needs. There are numerous distributions available, each with its own unique features and target audience. Popular options include Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, and CentOS. Consider factors such as ease of use, software availability, and community support when making your decision.
Create Installation Media:
Once you’ve chosen a distribution, download the ISO file from the official website. To install Linux on your computer, you’ll need to create installation media such as a USB drive or DVD. Follow the instructions provided by your chosen distribution to create bootable media.
Backup Your Data:
Before proceeding with the installation process, it’s crucial to back up any important data on your computer. While installing Linux generally doesn’t affect existing files on separate partitions or drives, it’s always better to be safe than sorry.
Boot from Installation Media:
Insert your bootable USB drive or DVD into your computer and restart it. Access the boot menu by pressing the designated key during startup (usually F12 or Delete). Select the appropriate option to boot from your installation media.
Begin Installation:
Once you’ve successfully booted from the installation media, you’ll be presented with an installation wizard. Choose your preferred language and follow the prompts to begin the installation process.
Partitioning:
During installation, you’ll be prompted to partition your hard drive. If you’re new to partitioning or unsure about specific settings, it’s recommended to choose automatic partitioning for simplicity. However, if you have specific requirements or wish to dual-boot with another operating system, you can manually configure your partitions.
Set Up User Account:
Next, you’ll be prompted to create a user account. Enter your desired username and password, which will be used to log in to your Linux system. It’s important to choose a strong password for enhanced security.
Choose Software Packages:
Depending on the distribution, you may have the option to select additional software packages during installation. This allows you to customize your Linux installation based on your specific needs and preferences. Choose the packages that align with your intended use of the operating system.
Complete Installation:
After selecting software packages, the installation process will continue. Sit back and let the installer do its work. The duration of the installation process may vary depending on your hardware specifications and chosen distribution.
Reboot and Enjoy Linux:
Once the installation is complete, you’ll be prompted to reboot your computer. Remove the installation media and let your system boot into Linux. Congratulations! You’ve successfully installed Linux on your computer.
Final Thoughts:
Installing Linux opens up a world of possibilities for users seeking an alternative operating system that is free, secure, and highly customizable. By following this step-by-step guide, you can confidently install Linux on your computer and embark on a journey into the open-source realm.
Remember, Linux offers a vast community of users who are always ready to provide support and guidance should you encounter any issues along the way. Embrace this new adventure with enthusiasm as you explore all that Linux has to offer!
8 Essential Tips for Installing Linux on Your Computer: A Guide for Beginners
- Research the different distributions of Linux and decide which one is best for you.
- Ensure your computer meets the minimum system requirements for the chosen distribution.
- Download and create a bootable installation media such as a USB drive or DVD/CD-ROM.
- Back up any important data on your computer before installing Linux, in case something goes wrong during the process.
- Set up your BIOS or UEFI settings to boot from your installation media, then reboot your computer with it inserted into a USB port or DVD/CD-ROM drive respectively.
- Follow the instructions on screen to install Linux onto your machine, including setting up partitions and formatting drives if necessary.
- Configure user accounts during installation, ensuring that you set secure passwords for each account created on the system (and remember them!).
- Once finished, remove any installation media from your device and reboot for the first time – you should now be running Linux!
Research the different distributions of Linux and decide which one is best for you.
Researching Linux Distributions: Finding the Perfect Fit
When it comes to installing Linux, one of the crucial steps that often gets overlooked is researching and selecting the right distribution for your needs. With a wide range of options available, each with its own strengths and characteristics, taking the time to evaluate and choose the best distribution can greatly enhance your overall Linux experience. Let’s delve into why researching different distributions is essential and how it can benefit you.
Understanding Linux Distributions:
Linux distributions, also known as distros, are different variations of the Linux operating system. While they all share a common foundation, each distribution offers its own unique set of features, software packages, user interfaces, and community support. Some popular distributions include Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, and CentOS.
Identifying Your Needs:
Before diving into research, it’s important to identify your specific requirements and goals for using Linux. Are you a beginner looking for a user-friendly interface? Do you need specific software packages or development tools? Are you interested in a lightweight distribution for older hardware? By understanding your needs upfront, you can narrow down your search to distributions that align with your goals.
Researching Features and User Experience:
Once you have identified your needs, it’s time to explore different distributions and their features. Visit official websites or reputable online resources to gather information about each distribution’s user interface, available software packages, compatibility with hardware devices, system requirements, stability levels, community support forums or documentation.
Considering Ease of Use:
For newcomers to Linux, ease of use is often an important factor. Some distributions like Ubuntu or Linux Mint are designed with user-friendliness in mind and offer intuitive interfaces similar to other operating systems. On the other hand, if you prefer more control over customization options or have advanced technical skills already in place, there are distributions like Arch Linux or Gentoo that provide a more hands-on and customizable experience.
Community Support:
The Linux community is known for its strong support network. Consider the availability of online forums, documentation, and active user communities when researching distributions. A vibrant and helpful community can make your Linux journey smoother by providing assistance, troubleshooting tips, and sharing knowledge.
Testing Before Installation:
Once you’ve narrowed down your options to a few distributions that seem promising, consider testing them out before committing to an installation. Most Linux distributions offer live environments that allow you to run the operating system from a USB drive or DVD without installing it. This gives you an opportunity to experience the distribution firsthand, explore its features, and assess its compatibility with your hardware.
Making an Informed Decision:
Armed with knowledge about different distributions, their features, and user experiences, you can now make an informed decision on which one is best suited for you. Remember that there is no “one-size-fits-all” solution; what works for one person may not work for another. Choose a distribution that aligns with your needs, preferences, and technical expertise.
In conclusion, researching different distributions of Linux is a crucial step in ensuring a successful installation experience. By understanding your requirements and exploring various options available, you can find the perfect distribution that meets your needs while providing an enjoyable and efficient Linux journey. So take the time to research and choose wisely – your Linux adventure awaits!
Ensure your computer meets the minimum system requirements for the chosen distribution.
Ensuring Your Computer Meets the Minimum System Requirements for Installing Linux
When it comes to installing Linux on your computer, one crucial aspect to consider is whether your system meets the minimum requirements specified by the chosen distribution. Adhering to these requirements ensures a smooth installation process and optimal performance of your Linux operating system. Let’s delve into why this step is essential and how you can verify compatibility.
Each Linux distribution has its own set of minimum system requirements, which may vary depending on factors such as the desktop environment, software packages included, and intended use. These requirements typically encompass aspects like processor speed, RAM capacity, storage space, and graphics capabilities.
Firstly, let’s discuss the importance of meeting these minimum specifications. Failure to meet the requirements may result in a sluggish or unstable system that hampers your overall user experience. Insufficient RAM or an underpowered processor can lead to slow performance and difficulty running resource-intensive applications. Additionally, inadequate storage space may limit your ability to install necessary software or save files.
To ensure your computer meets the minimum system requirements for your chosen Linux distribution, follow these steps:
- Research: Visit the official website of the distribution you wish to install and locate their documentation or system requirements page. Here you’ll find detailed information about what specifications are necessary for a successful installation.
- Compare: Take note of your computer’s hardware specifications (processor speed, RAM capacity, available storage) and compare them to the listed minimum requirements for the distribution you’ve chosen. Ensure that your computer meets or exceeds these specifications.
- Check Compatibility: Pay attention to any specific hardware compatibility issues mentioned in the documentation. Some distributions may have certain limitations or recommendations regarding graphics cards or wireless network adapters, so it’s vital to be aware of these potential constraints.
- Upgrade if Necessary: If your computer falls short of meeting the minimum requirements, consider upgrading specific components such as RAM or storage capacity before proceeding with the installation. Upgrading your hardware can significantly improve the performance and usability of your Linux system.
By verifying that your computer meets the minimum system requirements, you set yourself up for a successful Linux installation and a more satisfying experience overall. It’s worth noting that while meeting the minimum requirements is essential, exceeding them can further enhance performance and provide a smoother user experience.
Remember, installing Linux opens up a world of possibilities, offering you an alternative operating system that is secure, flexible, and highly customizable. By ensuring your computer meets the minimum system requirements, you lay a solid foundation for enjoying all the benefits that Linux has to offer.
Download and create a bootable installation media such as a USB drive or DVD/CD-ROM.
Download and Create a Bootable Installation Media: Your Gateway to Linux
If you’re ready to dive into the world of Linux and experience the power and freedom it offers, one of the first steps is to download and create a bootable installation media. Whether you choose a USB drive or a DVD/CD-ROM, this tip will guide you through the process of preparing your computer for a Linux installation.
Why Download and Create a Bootable Installation Media?
A bootable installation media is essential for installing Linux on your computer. It allows you to start the installation process without modifying your existing operating system. By creating this media, you gain the ability to try out different distributions, install Linux on multiple machines, or reinstall it whenever needed.
Step 1: Choose Your Preferred Distribution
Before downloading anything, decide which Linux distribution suits your needs. There are numerous options available, each with its own strengths and focus areas. Consider factors like ease of use, software availability, community support, and specific requirements for your intended use.
Step 2: Download the ISO File
Once you’ve chosen a distribution, visit its official website and locate the download section. Look for an ISO file specifically designed for creating bootable media. The ISO file contains all the necessary files for installing Linux on your computer.
Step 3: Choose Your Media Type
Decide whether you want to create a bootable USB drive or use a DVD/CD-ROM as your installation media. USB drives are generally more convenient due to their reusability and faster installation speeds. However, if your computer lacks USB boot capability or if you prefer using DVDs/CDs, that’s also an option.
Step 4: Create Bootable Media
To create a bootable USB drive, you’ll need software like Rufus, Etcher, or UNetbootin. These tools allow you to select the downloaded ISO file and write it onto the USB drive, making it bootable. Follow the software’s instructions to complete the process.
If you prefer using a DVD/CD-ROM, use burning software like ImgBurn or Brasero. Insert a blank DVD/CD-ROM into your computer’s optical drive and select the ISO file within the burning software. Follow the prompts to create a bootable disc.
Step 5: Configure Your Computer’s Boot Order
Before starting the installation process, ensure that your computer is set to boot from your chosen installation media. Access your computer’s BIOS or UEFI settings by pressing the designated key during startup (commonly F2, F10, or Delete). Locate the “Boot” or “Boot Order” section and rearrange the boot order so that your chosen media is prioritized.
Step 6: Begin Linux Installation
With your bootable installation media ready and your computer configured correctly, restart your system. It should now boot from the USB drive or DVD/CD-ROM you created. Follow the on-screen instructions provided by your chosen Linux distribution to start installing Linux on your computer.
By following these steps to download and create a bootable installation media, you’re well on your way to exploring all that Linux has to offer. Enjoy the freedom, security, and vast range of software options that come with this open-source operating system. Happy Linux installation!
Back up any important data on your computer before installing Linux, in case something goes wrong during the process.
The Importance of Backing Up Your Data Before Installing Linux
When it comes to installing a new operating system like Linux, it’s always better to be safe than sorry. One crucial tip that should never be overlooked is to back up any important data on your computer before proceeding with the installation process. This simple precautionary step can save you from potential headaches and frustrations if something unexpected happens during the installation.
Installing a new operating system involves making changes to your computer’s hard drive partitions and file systems. While modern installation processes are generally reliable, there is always a small chance that errors or unforeseen issues could occur. In rare cases, these issues could result in data loss or corruption.
By backing up your important data before installing Linux, you ensure that even if something goes wrong during the installation process, you won’t lose vital files or valuable information. It acts as an insurance policy for your digital life, providing peace of mind and protection against unforeseen circumstances.
There are various ways to back up your data, depending on your preferences and the amount of data involved. You can use external storage devices such as external hard drives or USB flash drives to manually copy and store important files. Alternatively, you can take advantage of cloud storage services or backup software to automate the backup process.
Remember that “important data” may include personal documents, photos, videos, music files, bookmarks, email archives, and any other files that hold significant value for you. It’s better to err on the side of caution and back up more than you think is necessary rather than regretting not doing so later.
Taking a few moments to back up your data before installing Linux is a small investment of time compared to the potential loss or inconvenience that could arise from not doing so. It ensures that no matter what happens during the installation process – whether it’s a power outage, hardware failure, or an unforeseen software glitch – your valuable files remain safe and accessible.
So, before you embark on the exciting journey of installing Linux on your computer, make it a priority to back up your important data. Embrace the peace of mind that comes with knowing your files are protected, and proceed with confidence, knowing that you have taken all necessary precautions to safeguard your digital world.
Set up your BIOS or UEFI settings to boot from your installation media, then reboot your computer with it inserted into a USB port or DVD/CD-ROM drive respectively.
Setting up BIOS or UEFI for Linux Installation: A Crucial Step
When it comes to installing Linux on your computer, one crucial step is often overlooked: setting up your BIOS or UEFI settings to boot from your installation media. This step ensures that your computer recognizes and prioritizes the installation media, allowing you to proceed with the installation process smoothly. In this article, we’ll explore why this step is important and how to go about it.
BIOS or UEFI: Understanding the Basics
Before diving into the specifics, let’s briefly understand what BIOS and UEFI are. BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) and UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) are firmware interfaces that control the initial startup process of your computer. They provide low-level software instructions to interact with hardware components during boot-up.
Why Is Setting Up BIOS or UEFI Important?
By default, computers are typically set to boot from the internal hard drive. However, when installing Linux or any other operating system from external media such as a USB drive or DVD/CD-ROM, you need to change this setting. By configuring your BIOS or UEFI settings correctly, you ensure that your computer looks for the installation media first during startup.
How to Set Up Your BIOS or UEFI for Linux Installation
The exact steps for accessing and modifying your BIOS or UEFI settings may vary depending on your computer’s manufacturer and model. However, here’s a general guide:
- Start by inserting your Linux installation media into a USB port or DVD/CD-ROM drive.
- Restart your computer.
- As soon as it starts booting up, look for the key prompt displayed on the screen (e.g., “Press F2 to enter Setup” or “Press Del for BIOS settings”).
- Press the designated key promptly to access the BIOS or UEFI setup utility. If you miss the prompt, restart your computer and try again.
- Once in the setup utility, navigate through the menus using the arrow keys on your keyboard. Look for an option related to “Boot” or “Boot Order”.
- Select the option that allows you to modify the boot order or boot sequence.
- Set your installation media (USB or DVD/CD-ROM) as the primary boot device by moving it to the top of the list.
- Save your changes and exit the setup utility (usually done by pressing F10 and confirming).
- Your computer will now restart with the modified BIOS or UEFI settings, prioritizing your Linux installation media.
Final Thoughts
Taking a few minutes to set up your BIOS or UEFI settings correctly before installing Linux can save you time and frustration in the long run. By ensuring that your computer recognizes and boots from your installation media, you’ll be able to proceed smoothly with the Linux installation process.
Remember, if you encounter any issues during this setup process or have difficulty accessing your BIOS or UEFI settings, consult your computer’s user manual or manufacturer’s website for specific instructions tailored to your system.
With this important step completed, you’re now ready to embark on your Linux installation journey and explore all that this powerful open-source operating system has to offer!
Follow the instructions on screen to install Linux onto your machine, including setting up partitions and formatting drives if necessary.
Installing Linux: Following On-Screen Instructions for a Seamless Installation
When it comes to installing Linux on your machine, following the instructions on screen is key to ensure a smooth and successful installation process. The on-screen prompts will guide you through various steps, including setting up partitions and formatting drives if necessary. Let’s delve into why this tip is crucial and how it can help you install Linux effortlessly.
Setting up Partitions:
During the installation process, you may be prompted to set up partitions on your hard drive. Partitions allow you to divide your storage space into separate sections, each with its own file system. This can be particularly useful if you want to run multiple operating systems or separate your personal files from the system files.
By following the instructions on screen, you’ll be guided through partitioning your hard drive effectively. The installer will typically provide options such as automatic partitioning or manual partitioning. If you’re new to partitioning or unsure about specific settings, choosing automatic partitioning can simplify the process by automatically allocating space for the operating system and user files.
Formatting Drives:
In some cases, you may need to format drives before installing Linux. Formatting involves preparing a storage device by erasing any existing data and configuring it with a compatible file system that Linux can recognize.
The on-screen instructions will provide guidance on formatting drives if necessary. You’ll have options such as formatting the entire drive or selecting specific partitions for formatting. It’s important to note that formatting a drive will permanently erase any data stored on it, so ensure that you have backed up any important files before proceeding.
Following these instructions ensures that your drives are properly formatted and ready for installation, minimizing potential issues during the installation process.
Benefits of Following On-Screen Instructions:
By carefully following the instructions provided during the installation process, you can avoid common pitfalls and errors that may arise when installing an operating system like Linux. The prompts are designed to guide users through each step, ensuring that necessary configurations are made correctly.
Moreover, the on-screen instructions provide a consistent and reliable source of information, making it easier for users of all experience levels to install Linux. Whether you’re a seasoned Linux user or a beginner, the instructions will help you navigate through the installation process with confidence.
In conclusion, following the instructions on screen during the Linux installation process is crucial for a seamless and trouble-free experience. From setting up partitions to formatting drives, these instructions will ensure that your system is properly configured for Linux. So, grab your installation media, boot up your machine, and let the on-screen prompts be your trusted guide as you embark on your journey into the world of Linux.
Configure user accounts during installation, ensuring that you set secure passwords for each account created on the system (and remember them!).
Secure User Accounts: A Crucial Step in Installing Linux
When installing Linux on your computer, one crucial step that often gets overlooked is configuring user accounts during the installation process. It’s essential to set up secure passwords for each account created on the system and, equally important, to remember them.
Why Secure User Accounts Matter
User accounts serve as the gateway to your Linux system. By setting strong and unique passwords for each account, you enhance the overall security of your system. Weak or easily guessable passwords can leave your system vulnerable to unauthorized access, potentially compromising your personal data and the integrity of your operating system.
Setting Secure Passwords
During the installation process, when prompted to create user accounts, take a moment to craft strong and secure passwords. Here are some tips to help you create robust passwords:
Length: Aim for a minimum password length of eight characters or more. The longer the password, the harder it is to crack.
Complexity: Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters like symbols or punctuation marks. This mix increases the complexity of your password and makes it more difficult to guess.
Avoid Common Words: Avoid using easily guessable words or phrases as part of your password. Hackers often employ dictionary-based attacks that rely on common words or phrases.
Unique Passwords: Ensure that each user account has its own unique password rather than using a single password for all accounts. This prevents unauthorized access if one account is compromised.
Remembering Your Passwords
While setting secure passwords is essential, it’s equally important to remember them without compromising their security. Here are some suggestions:
Mnemonics: Create memorable phrases or sentences that can be converted into passwords using the first letter of each word in the phrase along with numbers and symbols.
Password Managers: Consider using a reputable password manager tool that securely stores your passwords in an encrypted format. This way, you only need to remember one master password.
Physical Notes: If you choose to write down your passwords, keep them in a secure location away from prying eyes and ensure that they are not easily associated with the accounts they correspond to.
Conclusion
Configuring user accounts during the Linux installation process and setting secure passwords for each account is a vital step in ensuring the overall security of your system. By following these guidelines, you significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect your personal data.
Remember, strong passwords are just one aspect of maintaining a secure system. Regularly updating software, enabling automatic security updates, and practicing safe browsing habits further enhance the security of your Linux installation. With these precautions in place, you can enjoy a safe and worry-free experience using Linux.
Once finished, remove any installation media from your device and reboot for the first time – you should now be running Linux!
Congratulations! You have successfully completed the installation process and are now ready to explore the world of Linux. But before you dive in, there is one crucial step left to ensure a smooth transition.
After the installation is complete, it’s important to remove any installation media, such as USB drives or DVDs, from your computer. This step ensures that your system boots directly from the newly installed Linux operating system rather than relying on external media.
Once you have removed the installation media, go ahead and reboot your computer. As it starts up again, you will witness the exciting moment when your machine transitions into a Linux-powered environment.
This first boot into Linux signifies a new beginning, where you can unleash the power of open-source software and experience the freedom and flexibility that Linux offers. From this point forward, your computer will be running on Linux, ready for you to explore its vast array of features and applications.
Remember to familiarize yourself with the new user interface and take some time to customize your settings according to your preferences. Take advantage of the extensive software repositories available for Linux distributions, allowing you to install various applications tailored to your needs.
If you encounter any difficulties or have questions along the way, don’t hesitate to seek support from online forums or communities dedicated to helping Linux users. The Linux community is known for its helpfulness and willingness to assist newcomers.
So go ahead, remove that installation media and reboot your device with excitement. Welcome to the world of Linux – a powerful operating system that empowers users with freedom, security, and endless possibilities!