Linux CentOS: Power and Stability in an Open-Source Operating System
Linux CentOS, a popular distribution of the Linux operating system, has gained a reputation for its power, stability, and reliability. With its strong focus on security and long-term support, CentOS has become a go-to choice for both enterprise-level deployments and individual users seeking a robust and flexible operating system.
CentOS, derived from the freely available source code of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), inherits many of the strengths that have made RHEL a trusted solution in the business world. It provides a solid foundation for server environments, offering exceptional performance and scalability. Whether you’re running web servers, database servers, or other critical applications, CentOS delivers the stability and efficiency required to handle demanding workloads.
One of the key advantages of CentOS is its commitment to long-term support. Unlike some other Linux distributions that frequently release major updates or introduce radical changes, CentOS takes a more conservative approach. This means that once you have your system up and running with CentOS, you can rely on it to remain stable and secure for an extended period without disruptive changes. This is particularly advantageous for businesses that value consistency and predictability in their IT infrastructure.
Security is another area where CentOS shines. The development team behind CentOS actively monitors security vulnerabilities and promptly releases patches to address them. Combined with its inherent security features like SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux) and built-in firewall capabilities, CentOS provides a robust defense against potential threats. This makes it an excellent choice for organizations handling sensitive data or requiring stringent security measures.
CentOS’s popularity also stems from its extensive package repository known as EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux). EPEL offers an extensive collection of additional software packages beyond what comes pre-installed with the distribution. This allows users to easily expand their system’s capabilities by installing various applications and tools tailored to their specific needs.
Moreover, CentOS benefits from being part of the wider Linux community. Its large and active user base means that help and support are readily available. Online forums, documentation, and user groups provide a wealth of knowledge and assistance for troubleshooting, customization, or exploring new possibilities within the CentOS ecosystem.
Whether you are an experienced system administrator or a Linux enthusiast looking to experiment, CentOS offers a stable and powerful platform to build upon. Its reliability, long-term support, security features, and vibrant community make it an ideal choice for both personal and professional use.
In conclusion, Linux CentOS stands as a testament to the power of open-source software. With its rock-solid stability, long-term support commitment, robust security features, and extensive package repository, CentOS continues to be a trusted choice for individuals and organizations seeking a reliable operating system that can handle diverse workloads with ease. Embrace the power of CentOS and unlock the potential of open-source technology in your computing journey.
9 Essential Tips for Securing and Optimizing CentOS
- Install the latest version of CentOS to ensure you have the most up-to-date security patches and features.
- Use a firewall such as iptables or firewalld to protect your system from external threats.
- Make sure you keep your system up to date by installing all available security updates regularly.
- Utilize SELinux (Security Enhanced Linux) for additional layer of protection against malicious activity on your system.
- Create separate user accounts with limited privileges for each user, including yourself, to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data and resources on your server.
- Configure secure SSH access with strong passwords and two-factor authentication if possible, as well as disabling root login via SSH for added security measures.
- Take regular backups of important data stored on the server in case of an unforeseen disaster or attack that could cause irreparable damage to your system files and databases etc..
- Monitor server performance regularly using tools like top, htop or glances so you can detect any abnormal activities which could indicate a potential attack or other malicious activity on your system before it’s too late!
- Securely store confidential information such as passwords in encrypted form instead of plain text format so that it is not easily readable by anyone who gains access to it without permission from you
Install the latest version of CentOS to ensure you have the most up-to-date security patches and features.
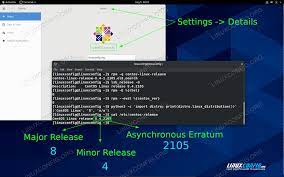
Stay Secure and Up-to-Date: Install the Latest Version of CentOS
When it comes to the security and functionality of your operating system, staying up-to-date is crucial. In the case of CentOS, one of the most popular Linux distributions, installing the latest version ensures that you have access to the most recent security patches and features, providing you with a strong foundation for a secure computing environment.
The CentOS development team works diligently to identify and address any vulnerabilities that may arise. By regularly releasing updates, they ensure that users can benefit from enhanced security measures that protect against emerging threats. These updates not only address known issues but also provide improvements in performance, stability, and compatibility.
Installing the latest version of CentOS is relatively straightforward. Begin by visiting the official CentOS website, where you can find the most recent release available for download. Take note of any specific requirements or recommendations provided by CentOS to ensure a smooth installation process.
Before proceeding with the installation, it’s always wise to back up any important data or configurations to avoid potential loss during the upgrade. Once you’re ready, follow the installation instructions provided by CentOS to complete the process.
By installing the latest version of CentOS, you are equipping yourself with an operating system that has been fine-tuned with updated security measures and cutting-edge features. This not only helps safeguard your system against potential threats but also ensures compatibility with modern software applications and hardware components.
Additionally, staying current with CentOS allows you to benefit from ongoing community support. The vibrant community surrounding CentOS constantly shares knowledge and provides assistance through forums, documentation, and user groups. This collaborative environment ensures that you have access to valuable resources when troubleshooting issues or seeking advice on how to optimize your system.
In conclusion, installing the latest version of CentOS is a proactive step towards maintaining a secure computing environment. By doing so, you gain access to critical security patches and feature enhancements while benefiting from ongoing community support. Take control of your system’s security and functionality by embracing the latest version of CentOS.
Use a firewall such as iptables or firewalld to protect your system from external threats.
Protect Your Linux CentOS System with a Firewall: Safeguarding against External Threats
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, ensuring the security of your Linux CentOS system is paramount. One effective way to fortify your system against external threats is by implementing a firewall. CentOS offers two popular firewall solutions: iptables and firewalld. By configuring and utilizing these tools, you can establish an additional layer of protection for your valuable data and resources.
Iptables, a powerful command-line utility, has long been the go-to firewall solution for many Linux users. It operates by filtering network traffic based on predefined rules that you set up. With iptables, you have granular control over incoming and outgoing connections, allowing you to define specific protocols, ports, IP addresses, or ranges that are permitted or denied access.
However, iptables can be quite complex for beginners due to its command-line interface and extensive rule syntax. This is where firewalld comes into play. Firewalld is a user-friendly alternative that provides a higher-level abstraction of the underlying iptables functionality. It simplifies the process of managing firewall rules by introducing concepts like zones and services.
Firewalld allows you to define zones (e.g., public, internal, or trusted) to categorize different network environments with varying security requirements. You can then assign specific services (e.g., HTTP or SSH) to these zones, automatically configuring the necessary rules for each service. This approach makes managing your firewall more intuitive and less error-prone.
Whether you choose iptables or firewalld as your preferred firewall solution on CentOS, there are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Regularly update your firewall rules: As new threats emerge or your network requirements change, it’s essential to review and update your firewall rules accordingly.
- Implement the principle of least privilege: Only allow network traffic that is explicitly required for your system’s operation. Restrict access to services and ports that are not necessary, reducing the potential attack surface.
- Monitor your firewall logs: Keep an eye on your firewall logs for any suspicious activity or attempts to breach your system’s security. Promptly investigate and respond to any anomalies.
- Consider using additional security measures: While firewalls provide an essential layer of protection, it’s beneficial to combine them with other security tools like intrusion detection systems (IDS) or virtual private networks (VPNs) for enhanced security.
By leveraging a firewall such as iptables or firewalld, you can significantly enhance the security of your Linux CentOS system. These tools help you regulate network traffic, control access to services, and safeguard against external threats. Take advantage of their capabilities and ensure that your valuable data and resources remain protected in today’s ever-evolving digital landscape.
Make sure you keep your system up to date by installing all available security updates regularly.
Keeping Your CentOS System Secure: The Importance of Regular Updates
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, maintaining the security of your operating system is paramount. When it comes to Linux CentOS, one of the most effective ways to safeguard your system is by regularly installing all available security updates. This simple yet crucial tip ensures that your CentOS environment remains protected against emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Security updates are released by the CentOS development team to address known vulnerabilities and strengthen the overall security of the operating system. These updates often include patches that fix potential weaknesses in system components, libraries, or software packages. By installing these updates promptly, you not only protect your system from potential exploits but also ensure its stability and optimal performance.
To keep your CentOS system up to date with the latest security patches, you can rely on the built-in package manager called YUM (Yellowdog Updater Modified). YUM simplifies the process of updating your system by automatically fetching and installing updates from official repositories. Running regular update commands, such as “yum update” or “yum upgrade,” will ensure that you have the most recent security fixes installed on your system.
By neglecting to install security updates, you leave your CentOS system vulnerable to potential attacks. Cybercriminals are constantly searching for weaknesses in operating systems and software applications to exploit. Regularly updating your system helps close these vulnerabilities before they can be targeted by malicious actors.
Furthermore, keeping your CentOS environment up to date demonstrates a proactive approach towards cybersecurity. It shows that you prioritize the protection of sensitive data and maintain a secure computing environment for yourself or your organization. This commitment to security not only safeguards against potential breaches but also helps maintain compliance with industry regulations and best practices.
In addition to security benefits, staying current with updates provides access to new features, bug fixes, and performance improvements. These enhancements can enhance productivity and provide a better user experience while using CentOS.
Remember that maintaining a secure Linux CentOS system is an ongoing process. Security updates are regularly released to address newly discovered vulnerabilities, so it is essential to make updating a regular part of your system maintenance routine. By dedicating a small amount of time to keeping your system up to date, you contribute to its overall security and help create a safer computing environment.
In conclusion, ensuring that you regularly install all available security updates on your Linux CentOS system is vital for maintaining its security, stability, and optimal performance. By embracing this tip and staying proactive in updating your system, you fortify your defences against potential threats and demonstrate a commitment to cybersecurity. Stay vigilant, keep your CentOS system up to date, and enjoy the peace of mind that comes with a secure computing environment.
Utilize SELinux (Security Enhanced Linux) for additional layer of protection against malicious activity on your system.
Enhance Security with SELinux on CentOS: Safeguarding Your System Against Malicious Activity
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats, it is crucial to employ robust measures to protect our systems and data. One such measure available to users of CentOS, a powerful Linux distribution, is SELinux (Security Enhanced Linux). By utilizing SELinux, you can add an additional layer of protection against malicious activity on your system.
SELinux is a security framework integrated into CentOS that provides mandatory access control (MAC) mechanisms. It goes beyond traditional discretionary access controls (DAC) by enforcing policies that define what actions processes and users are allowed to perform on the system. This granular level of control helps mitigate potential risks and limits the impact of security breaches.
When enabled, SELinux assigns labels to files, directories, processes, and network ports based on predefined security policies. These labels determine which actions are permitted or denied for each entity within the system. By default, SELinux operates in enforcing mode, meaning it actively enforces the defined policies and denies any unauthorized attempts.
One significant advantage of SELinux is its ability to confine processes within strict boundaries. This confinement prevents compromised or malicious applications from accessing sensitive resources or executing unauthorized actions. Even if an attacker manages to exploit a vulnerability in an application running under SELinux, the impact will be limited due to the restrictions imposed by the security policies.
Implementing SELinux on CentOS requires some configuration and understanding of its policies. However, once properly set up, it provides a powerful defense mechanism against various types of attacks such as privilege escalation, file tampering, or unauthorized network access.
To make the most of SELinux on CentOS:
- Familiarize yourself with SELinux policies: Understand how they work and what they aim to achieve. The CentOS documentation and online resources provide valuable information to help you get started.
- Configure SELinux for your specific needs: CentOS offers different SELinux modes, including enforcing, permissive, and disabled. Choose the appropriate mode based on your security requirements and system usage.
- Regularly update SELinux policies: As new vulnerabilities and threats emerge, the SELinux community releases updated policies to address them. Keep your system up to date to benefit from the latest security enhancements.
- Monitor SELinux alerts: Pay attention to alerts generated by SELinux, as they can provide valuable insights into potential security issues or policy violations. Investigate and take appropriate action when necessary.
By leveraging the power of SELinux on CentOS, you fortify your system’s defenses against malicious activity. This additional layer of protection helps safeguard your data, applications, and infrastructure from potential breaches. Embrace the proactive approach offered by SELinux and enjoy enhanced peace of mind in an increasingly interconnected world.
Remember, while SELinux is a powerful security tool, it is not a substitute for other best practices such as regular software updates, strong passwords, and secure network configurations. A comprehensive approach to cybersecurity involves multiple layers of defense working together synergistically to create a robust shield against threats.
Create separate user accounts with limited privileges for each user, including yourself, to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data and resources on your server.
Enhance Security with Separate User Accounts on CentOS
When it comes to securing your Linux CentOS server, one crucial step is to create separate user accounts with limited privileges for each user, including yourself. By implementing this practice, you can effectively prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data and resources, bolstering the overall security of your server.
Creating individual user accounts ensures that each person accessing the server has their own unique credentials. This approach helps in tracking and auditing activities, as well as granting specific permissions based on the user’s role or responsibilities. By assigning limited privileges to each account, you can control what actions each user can perform and restrict access to critical system files or directories.
To begin, log in to your CentOS server with administrative privileges. Once logged in, open a terminal window and follow these steps:
Create a new user account using the “adduser” command:
“`
sudo adduser username
“`
Replace “username” with the desired name for the new account.
Set a secure password for the newly created account:
“`
sudo passwd username
“`
Follow the prompts to enter and confirm the password.
Grant administrative privileges (optional):
If you want to grant administrative rights (sudo access) to a specific user, add them to the “wheel” group:
“`
sudo usermod -aG wheel username
“`
Repeat these steps for each additional user you want to create.
By creating separate accounts for each user, you ensure that individual credentials are required for accessing your server. This prevents unauthorized users from gaining unrestricted access or accidentally modifying critical system files.
Furthermore, utilizing limited privileges adds an extra layer of security by restricting certain actions that can potentially harm your system or compromise sensitive data. Each user can only perform operations within their designated scope of permissions, reducing the risk of unintentional mistakes or malicious activities.
Remember, it’s essential to regularly review and update user accounts as needed. Remove any unnecessary accounts or adjust permissions when roles change within your organization. By actively managing user accounts, you maintain a secure environment and minimize the potential for unauthorized access.
In conclusion, creating separate user accounts with limited privileges on your Linux CentOS server is a fundamental security measure. By implementing this practice, you establish a strong barrier against unauthorized access to sensitive data and resources. Take control of your server’s security today by following these steps and safeguarding your valuable information from potential threats.
Enhancing Security on Linux CentOS: Secure SSH Access with Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication
In today’s digital landscape, ensuring the security of our systems is of paramount importance. When it comes to Linux CentOS, one effective way to bolster security is by configuring secure SSH (Secure Shell) access. By following a few simple steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect your system from potential threats.
First and foremost, it is crucial to set strong passwords for SSH authentication. Weak or easily guessable passwords can leave your system vulnerable to brute-force attacks. Aim for complex passwords that include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Additionally, avoid reusing passwords across different accounts or services to prevent potential credential leaks from compromising your system’s security.
Moreover, consider implementing two-factor authentication (2FA) for SSH access if possible. 2FA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to provide a second form of verification in addition to their password. This typically involves using a time-based one-time password (TOTP) generator or receiving verification codes via SMS or email. By enabling 2FA, even if an attacker manages to obtain the user’s password, they would still need the second factor to gain access.
Another important measure is disabling root login via SSH. The root account has elevated privileges on a Linux system and is often targeted by malicious actors. By disabling direct root login via SSH and instead using a regular user account with sudo privileges, you limit the potential attack surface and make it more difficult for attackers to compromise your system.
To implement these security measures on CentOS, follow these steps:
- Edit the SSH configuration file located at /etc/ssh/sshd_config using a text editor such as nano or vi.
- Locate the line that reads “PermitRootLogin” in the file.
- Change the value from “yes” to “no” to disable root login via SSH.
- Save the changes and exit the text editor.
- Restart the SSH service using the command: “sudo systemctl restart sshd”.
Additionally, if you wish to enable two-factor authentication, there are various methods available. One popular option is using Google Authenticator, which provides TOTP codes for authentication. Install the necessary packages and configure it following detailed guides available online.
By configuring secure SSH access with strong passwords, implementing two-factor authentication, and disabling root login via SSH on your CentOS system, you significantly enhance its security posture. These measures act as formidable barriers against potential threats and unauthorized access attempts. Remember to regularly update your system’s software and keep an eye on security advisories to stay ahead of emerging vulnerabilities.
Investing time in securing your Linux CentOS system today will undoubtedly pay off in terms of peace of mind and protection against potential cyber threats tomorrow. Stay vigilant, follow best practices, and enjoy a more secure computing environment with Linux CentOS.
Take regular backups of important data stored on the server in case of an unforeseen disaster or attack that could cause irreparable damage to your system files and databases etc..
Secure Your Data: The Importance of Regular Backups in CentOS
In the world of Linux CentOS, where stability and reliability are paramount, safeguarding your important data should be a top priority. While the operating system itself is renowned for its resilience, it’s crucial to take proactive measures to protect your valuable files and databases from unforeseen disasters or malicious attacks. That’s where regular backups come into play.
Taking regular backups of your important data stored on the server is a fundamental practice that can save you from potential headaches and heartaches down the line. By creating copies of your critical files and databases, you ensure that even if disaster strikes, you have a safety net to fall back on.
Imagine a scenario where your system experiences a catastrophic failure, such as hardware malfunctions or software corruption. Without proper backups in place, you could lose crucial business documents, customer information, or years’ worth of hard work. Similarly, in the event of a cyber attack or malware infection that compromises your data integrity, having recent backups allows you to restore your systems to a known good state.
CentOS provides various tools and methods to facilitate smooth backup processes. One popular option is using the powerful rsync utility combined with cron jobs for automated scheduling. With rsync, you can efficiently synchronize files between different directories or even across multiple servers while preserving their permissions and attributes.
Another approach is leveraging backup solutions like Bacula or Amanda that offer comprehensive backup management capabilities. These tools allow you to create customized backup policies, automate backups at specified intervals, and perform incremental backups to minimize storage requirements.
When considering backups in CentOS, it’s essential to determine where to store your backup copies securely. Utilizing external storage devices such as external hard drives or network-attached storage (NAS) devices ensures physical separation between your primary system and backups. Additionally, cloud-based storage solutions offer an off-site backup option that protects against local disasters like fire or theft.
Remember that backups are only effective if they are regularly tested and verified. Periodically restoring data from your backups helps ensure their integrity and confirms that you can successfully recover your important files when needed.
In conclusion, taking regular backups of your important data in CentOS is not just a recommended practice; it’s a crucial step in securing your digital assets. By implementing a robust backup strategy, you mitigate the risks associated with system failures, cyber threats, or accidental data loss. Embrace the power of backups and rest easy knowing that your valuable information is safeguarded against unforeseen disasters or attacks.
Protect what matters most – start backing up today!
Monitor Server Performance Regularly: A Crucial Step for Linux CentOS Security
In today’s digital landscape, ensuring the security of your server is of paramount importance. Linux CentOS, known for its stability and reliability, offers a robust platform for hosting critical applications and data. However, even with a secure operating system like CentOS, it is essential to proactively monitor server performance to detect any abnormal activities that could indicate a potential attack or malicious activity.
Regularly monitoring server performance allows you to gain valuable insights into the health and behavior of your system. By using tools like top, htop, or glances, you can obtain real-time information about resource usage, process activity, and system metrics. These tools provide an overview of CPU usage, memory utilization, disk I/O operations, network traffic, and more.
By keeping a close eye on these performance indicators, you can quickly identify any unusual patterns or spikes that may suggest an ongoing attack or unauthorized activity. For instance, abnormally high CPU usage by an unknown process could indicate the presence of malware or a malicious script running on your server. Similarly, unexpected network traffic from unfamiliar sources might be a sign of attempted intrusion.
Early detection is crucial in preventing potential security breaches or minimizing their impact. By monitoring server performance regularly and diligently reviewing the data provided by monitoring tools, you can proactively identify signs of compromise or suspicious activities before they escalate into full-scale attacks.
In addition to security benefits, monitoring server performance also helps optimize resource allocation and improve overall system efficiency. By identifying processes that consume excessive resources or identifying bottlenecks in disk I/O or network bandwidth usage through monitoring tools, you can make informed decisions about resource allocation and take necessary actions to optimize performance.
To ensure effective monitoring:
- Set up regular intervals for checking server performance using tools such as top (a command-line tool), htop (a more user-friendly alternative), or glances (a comprehensive monitoring tool).
- Familiarize yourself with the normal behavior of your system by establishing baseline performance metrics. This will help you quickly identify any deviations from the norm.
- Actively monitor resource usage, process activity, and system metrics for any unusual patterns or spikes that could indicate potential security threats or abnormal activities.
- Regularly review logs and alerts generated by monitoring tools to stay informed about any critical events or anomalies that require immediate attention.
By incorporating regular server performance monitoring into your security practices, you can enhance the protection of your Linux CentOS system. Stay vigilant, be proactive, and ensure the ongoing reliability and security of your server environment.
Securely store confidential information such as passwords in encrypted form instead of plain text format so that it is not easily readable by anyone who gains access to it without permission from you
Protecting Confidential Information: Securing Passwords in Linux CentOS
In today’s digital age, safeguarding confidential information is of utmost importance. When it comes to Linux CentOS, a crucial tip for enhancing security is storing sensitive data, such as passwords, in encrypted form rather than plain text format. This simple yet effective practice ensures that even if someone gains unauthorized access to your system, they won’t be able to easily read or misuse your valuable information.
By storing passwords in encrypted form, you add an extra layer of protection against potential threats. Encryption is the process of transforming data into an unreadable format using mathematical algorithms. Only authorized individuals with the proper decryption key can convert the encrypted data back into its original readable form.
Thankfully, Linux CentOS provides various tools and techniques to help you securely store passwords and other confidential information. One widely used method is hashing passwords using strong cryptographic algorithms like SHA-256 or bcrypt. Hashing involves converting a password into a fixed-length string of characters that cannot be reversed to obtain the original password. When a user enters their password during authentication, it gets hashed and compared with the stored hash value. If they match, access is granted.
Another approach is to use tools like GnuPG (GNU Privacy Guard) or OpenSSL to encrypt sensitive files containing passwords or other confidential data. These tools employ robust encryption algorithms to protect your information from unauthorized access. You can create an encrypted file or container and then securely store it on your system or transfer it across different devices without worrying about exposing the contents.
It’s important to note that while encryption significantly enhances security, it’s equally crucial to protect the encryption keys themselves. Ensure that only authorized individuals have access to these keys and implement secure storage measures for them.
By adopting this best practice of securely storing confidential information in encrypted form on Linux CentOS, you fortify your system against potential breaches and unauthorized access attempts. Remember that securing passwords is just one aspect of a comprehensive security strategy. Regularly updating your system, implementing strong access controls, and following other security best practices are equally important in maintaining a secure computing environment.
In conclusion, encryption is an essential tool in protecting sensitive information such as passwords. Linux CentOS offers robust encryption capabilities that allow you to store confidential data securely. By implementing this tip and making encryption a standard practice, you take a significant step towards safeguarding your valuable information from prying eyes and unauthorized access. Prioritize security, protect your data, and enjoy the peace of mind that comes with knowing your confidential information is safe within your Linux CentOS environment.