The Powerhouse Behind Linux: Exploring the Linux Kernel
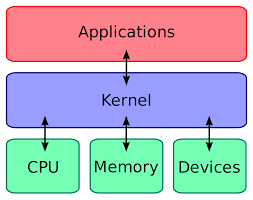
Linux, an operating system renowned for its stability, security, and versatility, owes its success to a critical component known as the Linux kernel. Often referred to as the “heart” of Linux, the kernel is responsible for managing hardware resources and providing a bridge between software applications and computer hardware.
At its core, the Linux kernel is an open-source project that embodies the spirit of collaboration and community-driven innovation. Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, it has since evolved into a powerful force in the world of computing. Thousands of dedicated developers from around the globe contribute to its continuous improvement and expansion.
One of the key strengths of the Linux kernel lies in its adaptability. It supports a wide range of hardware architectures, making it compatible with various devices such as desktop computers, servers, smartphones, embedded systems, and even supercomputers. This flexibility allows users to choose their preferred hardware while still benefiting from the robustness and reliability of Linux.
The kernel’s architecture is designed to maximize performance while ensuring stability. It employs a modular structure that allows for easy customization and scalability. Different modules can be added or removed as needed without compromising system integrity or functionality. This modularity also enables efficient maintenance and updates, ensuring that security patches and new features can be seamlessly integrated into existing installations.
Security is another area where the Linux kernel excels. With its strong emphasis on open-source development, vulnerabilities are quickly identified and resolved by a vast community of developers who scrutinize every line of code. Regular security updates are released promptly to address any potential risks or exploits. This commitment to security has contributed significantly to establishing Linux as a trusted platform for mission-critical systems in industries such as finance, healthcare, and government.
Moreover, performance optimization is an ongoing focus within the Linux kernel development community. Through continuous refinement and enhancements to various subsystems such as memory management, process scheduling, and input/output operations, the kernel strives to deliver exceptional performance across a wide range of workloads. This dedication to performance has made Linux a preferred choice for high-performance computing and demanding applications.
The Linux kernel’s success is not limited to technical achievements alone. Its open-source nature fosters a vibrant community that encourages collaboration, knowledge sharing, and collective problem-solving. Developers, enthusiasts, and users come together to exchange ideas, report issues, and contribute improvements back to the project. This collaborative ecosystem ensures that Linux remains at the forefront of innovation while addressing the evolving needs of its diverse user base.
In conclusion, the Linux kernel stands as a testament to the power of open-source development. Its adaptability, security focus, performance optimization, and strong community support have propelled Linux to become one of the most widely used operating systems in the world. As technology continues to advance, we can expect the Linux kernel to evolve further, driving innovation and shaping the future of computing for years to come.
Advantages of the Linux Kernel: Embracing Open Source, Enhancing Security, Ensuring Reliability, Enabling Scalability, and Promoting Compatibility
- Open Source
- Security
- Reliability
- Scalability
- Compatibility
Challenges and Drawbacks of the Linux Kernel: Complexity, Limited Support, Security Vulnerabilities, and Compatibility Issues
- Complexity
- Limited Support
- Security Vulnerabilities
- Compatibility Issues
Open Source
Open Source: Unleashing the Power of the Linux Kernel
One of the greatest strengths of the Linux kernel lies in its open-source nature. Unlike proprietary software, the Linux kernel source code is freely available for anyone to view, modify, and distribute. This openness has fostered a thriving ecosystem where a diverse community of developers collaborates to enhance and customize the kernel for various applications.
The beauty of open source lies in its inclusivity. It allows developers from all backgrounds and skill levels to contribute their expertise and creativity to the Linux kernel’s development. This collaborative approach has resulted in a wealth of improvements, innovations, and optimizations that benefit users worldwide.
The ability to view and modify the code gives developers unparalleled control over their systems. They can tailor the Linux kernel to suit specific requirements, whether it’s optimizing performance for high-performance computing, customizing drivers for unique hardware configurations, or tailoring security features for specialized environments. This flexibility enables Linux to be used in an extensive range of applications, from embedded systems and servers to smartphones and supercomputers.
Furthermore, open source encourages transparency and accountability. With the code freely accessible, potential vulnerabilities can be identified more readily by a large community of users and developers who actively scrutinize it. This collective effort promotes rapid detection and resolution of security issues, ensuring that Linux remains robust and secure.
The collaborative nature of open source also fosters knowledge sharing and continuous learning. Developers can learn from each other’s contributions, share best practices, and collectively solve complex problems. This collaborative spirit extends beyond just coding; it encompasses documentation efforts, bug reporting, testing initiatives, and user support forums. The result is a vibrant community that empowers individuals while fostering a sense of belonging.
Open source has become a driving force behind technological innovation. Many groundbreaking technologies have emerged through open-source collaboration within the Linux ecosystem. From containerization with Docker to cloud computing platforms like OpenStack, these advancements have revolutionized the way we develop, deploy, and manage software.
In conclusion, the open-source nature of the Linux kernel is a fundamental pillar of its success. It enables a diverse community of developers to contribute their expertise and customize the kernel for a wide range of applications. This collaborative approach not only empowers individuals but also fosters transparency, accountability, and continuous learning. The Linux kernel’s open-source philosophy has propelled it to become a powerful and versatile operating system that continues to shape the future of computing.
Security
The Unyielding Shield: The Security Advantages of the Linux Kernel
When it comes to security, the Linux kernel stands tall as a fortress, offering robust protection for mission-critical systems where safeguarding sensitive data is of utmost importance. With a wide array of built-in security features, Linux has earned a reputation as one of the most secure operating systems available today.
At the heart of its security prowess lies the Linux kernel, which serves as the guardian of your digital assets. One notable advantage is its implementation of access control lists (ACLs), which provide granular control over file and directory permissions. This ensures that only authorized users or processes can access specific resources, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
Firewalls are another integral part of the Linux kernel’s security arsenal. With powerful firewall capabilities such as iptables and nftables, Linux allows administrators to define and enforce network traffic rules, protecting systems from malicious activities and unauthorized network connections. These firewalls act as virtual gatekeepers, meticulously examining incoming and outgoing traffic to prevent potential threats from infiltrating your system.
Encryption is a fundamental aspect of modern-day security practices, and the Linux kernel excels in this area too. It offers robust encryption mechanisms that protect sensitive information both at rest and in transit. Whether it’s encrypting files using tools like dm-crypt or securing network communications with protocols like SSL/TLS, Linux ensures that your data remains confidential and inaccessible to unauthorized entities.
User authentication is a critical component in any secure system, and the Linux kernel incorporates various authentication methods to verify user identities. From traditional password-based authentication to more advanced techniques like public key cryptography or multi-factor authentication (MFA), Linux provides flexible options for ensuring that only legitimate users can access protected resources.
Moreover, one of the key advantages of using an open-source operating system like Linux is its transparent development process. With countless eyes scrutinizing every line of code, vulnerabilities are quickly identified and addressed by the vibrant Linux community. This collaborative effort ensures that security patches and updates are promptly released, bolstering the overall security posture of the Linux kernel.
The Linux kernel’s commitment to security makes it an ideal choice for organizations operating in high-stakes environments. Whether it’s financial institutions safeguarding customer data, healthcare providers protecting patient records, or government agencies securing sensitive information, the Linux kernel provides a solid foundation for building secure systems that can withstand sophisticated threats.
In an era where cyberattacks are becoming increasingly prevalent, having a secure operating system is paramount. The Linux kernel’s robust security features, including access control lists, firewalls, encryption, and user authentication mechanisms, make it a formidable fortress against potential threats. By choosing Linux as the foundation for your critical systems, you can rest assured knowing that your data is protected by an unwavering shield of security.
Reliability
The Linux Kernel: A Reliable Backbone for Industrial Environments
When it comes to reliability, the Linux kernel stands as a shining example in the world of operating systems. Designed with robustness and stability in mind, the Linux kernel has proven its mettle, making it an ideal choice for industrial environments where downtime is simply not an option.
In industrial settings, where critical processes and systems are at play, reliability is paramount. Any interruption or failure can have severe consequences, leading to financial losses, production delays, and potential safety hazards. This is where the Linux kernel truly shines.
The Linux kernel’s architecture and design principles prioritize stability and fault tolerance. It incorporates features such as process isolation, memory protection mechanisms, and error handling mechanisms that help prevent system crashes and ensure smooth operation even under heavy workloads.
Furthermore, the Linux kernel’s ability to handle hardware resources efficiently plays a crucial role in enhancing reliability. It manages system resources effectively, preventing resource conflicts that could lead to system instability or failures. This careful resource management ensures that critical processes can run smoothly without interference from other applications or services.
Another factor contributing to the reliability of the Linux kernel is its extensive testing and validation procedures. The open-source nature of Linux allows for a vast community of developers worldwide to contribute to its development and testing process. This collaborative effort results in rigorous testing on various hardware platforms and configurations, ensuring that potential issues are identified early on and promptly addressed before they impact real-world deployments.
Moreover, the timely release of security updates is another testament to the reliability of the Linux kernel. The dedicated community behind its development works tirelessly to identify vulnerabilities promptly and provide patches or updates swiftly. This proactive approach ensures that industrial systems powered by Linux remain secure against emerging threats.
The reliability of the Linux kernel has made it a popular choice across various industries such as manufacturing plants, power generation facilities, transportation systems, and more. Its ability to handle critical tasks with minimal downtime has earned the trust of professionals who rely on uninterrupted operations.
In conclusion, the Linux kernel’s focus on reliability makes it an excellent choice for industrial environments where downtime can have significant repercussions. Its robust architecture, efficient resource management, extensive testing, and proactive security measures set it apart as a reliable backbone for critical systems. With the Linux kernel at its core, industrial environments can operate with confidence, knowing that their systems are built on a foundation that prioritizes stability and resilience.
Scalability
The Linux Kernel: Unleashing the Power of Scalability
One of the key advantages of the Linux kernel is its remarkable scalability. Whether you need a lightweight system for an embedded device or a robust platform to run large-scale enterprise applications on powerful servers, the Linux kernel can effortlessly accommodate your needs.
At its core, the Linux kernel is designed to be flexible and adaptable. It can seamlessly scale up or down depending on the requirements of the application or system it supports. This scalability empowers developers and administrators to tailor their Linux-based solutions to fit a wide range of computing environments.
For resource-constrained devices such as embedded systems, where memory and processing power are limited, the Linux kernel can be optimized to run efficiently on these devices. Through careful configuration and customization, unnecessary components can be stripped away, resulting in a lean and streamlined operating system that conserves resources while still providing essential functionality.
On the other end of the spectrum, when dealing with high-performance servers running large enterprise applications, the Linux kernel shines just as brightly. Its scalability allows it to harness the full potential of modern hardware architectures, leveraging multiple processors, vast amounts of memory, and advanced storage technologies. This enables businesses to build robust and scalable infrastructures capable of handling demanding workloads with ease.
The ability of the Linux kernel to scale seamlessly across different environments brings numerous benefits. It ensures that software developed for smaller systems can easily transition to larger deployments without requiring major code rewrites or architectural changes. This compatibility reduces development time and costs while providing a consistent experience across different platforms.
Furthermore, this scalability also promotes efficient resource utilization. By matching system resources with application requirements, organizations can optimize their infrastructure’s performance while keeping costs in check. Whether it’s running a single service on a small device or managing complex distributed systems across multiple servers, the Linux kernel’s ability to scale ensures optimal resource allocation for maximum efficiency.
The open-source nature of the Linux community plays a significant role in enhancing the scalability of the Linux kernel. A vast network of developers and contributors continually works towards improving and expanding its capabilities. This collaborative effort ensures that the Linux kernel remains at the forefront of scalability advancements, adapting to new technologies and evolving demands.
In conclusion, the Linux kernel’s scalability is a testament to its versatility and adaptability. From embedded devices to powerful servers, it effortlessly accommodates a wide range of computing environments. This flexibility not only simplifies development and deployment but also optimizes resource utilization, enabling businesses to build efficient and cost-effective solutions. With its robust scalability, the Linux kernel continues to empower organizations across industries, driving innovation and transforming the way we approach computing.
Compatibility
Linux Kernel: Unleashing Compatibility for Custom Solutions
One of the standout advantages of the Linux kernel is its exceptional compatibility with a vast array of hardware components. With support for multiple hardware architectures and an extensive range of device drivers, Linux offers a level of flexibility that empowers users to create custom solutions tailored to their specific requirements, all without the need for expensive proprietary hardware.
The Linux kernel’s compatibility extends across a wide spectrum of devices, including network cards, graphics cards, storage devices, and more. This broad support ensures that users can leverage their existing hardware investments or choose from a diverse range of affordable options when building their systems. Whether it’s a home desktop, a server farm, or an embedded system, Linux provides the foundation for seamless integration with various hardware components.
By embracing open standards and providing comprehensive driver support, the Linux kernel eliminates many of the compatibility barriers that can hinder technological advancements. This means that users are not limited to specific vendors or proprietary solutions but can instead explore a wider range of choices. This freedom allows for greater innovation and fosters healthy competition among manufacturers, ultimately driving down costs and increasing accessibility.
Moreover, the Linux community actively contributes to developing and maintaining device drivers for numerous hardware components. This collaborative effort ensures that new devices are supported promptly and efficiently integrated into the kernel. Users can rely on this collective expertise to ensure their systems remain up-to-date and compatible with cutting-edge technologies.
The ability to create custom solutions without being tied down by proprietary hardware is particularly beneficial in various contexts. For businesses seeking cost-effective IT infrastructure solutions, Linux provides an excellent platform on which to build tailored systems that meet specific needs. It enables organizations to optimize their resources by repurposing existing equipment or selecting affordable yet reliable components.
In addition, developers working on niche projects or specialized applications can take advantage of Linux’s compatibility features to create unique solutions. The ability to choose from a wide range of compatible hardware components simplifies the development process and allows for greater experimentation and innovation. This flexibility is particularly valuable in research environments, where custom hardware configurations are often required.
The Linux kernel’s compatibility not only empowers users to create custom solutions but also contributes to the overall growth and advancement of technology. By embracing open standards and supporting a diverse range of hardware, Linux fosters an environment of collaboration and innovation. It encourages manufacturers to develop high-quality, compatible products, ultimately benefiting users with increased choice, affordability, and accessibility.
In conclusion, the Linux kernel’s compatibility with multiple hardware architectures and extensive device driver support unlocks a world of possibilities for users seeking custom solutions. Whether it’s building cost-effective IT infrastructure or developing specialized applications, Linux provides the foundation for seamless integration with a wide variety of hardware components. With its commitment to openness and collaboration, the Linux kernel continues to drive innovation while empowering users with unmatched compatibility options.
Complexity
Navigating the Complexity: Unraveling the Linux Kernel
The Linux kernel, renowned for its power and versatility, is not without its challenges. One of the notable downsides that users often encounter is its inherent complexity. As a sophisticated piece of software, the Linux kernel can be daunting to learn and configure, especially for those new to the world of operating systems.
The intricacies of the Linux kernel stem from its robustness and ability to support a vast array of hardware architectures and system configurations. This flexibility comes at the cost of increased complexity, as it requires a deeper understanding of various subsystems, drivers, and configuration options.
For newcomers or casual users seeking a plug-and-play experience, this complexity can be overwhelming. The learning curve associated with understanding the inner workings of the Linux kernel may deter some individuals from exploring its full potential. Configuring and optimizing the kernel for specific hardware or software requirements can be a time-consuming task that demands technical expertise.
However, it’s important to note that while the Linux kernel may initially appear complex, there are resources available to help users overcome these challenges. Online communities, forums, and documentation provide valuable insights into configuring and troubleshooting issues related to the kernel. Additionally, various graphical tools have been developed to simplify certain aspects of managing the Linux kernel.
Moreover, as open-source software thrives on collaboration and community support, individuals can seek assistance from experienced users who are often eager to share their knowledge and offer guidance.
While complexity can be seen as a disadvantage of the Linux kernel, it’s worth noting that this very complexity is what enables its unparalleled flexibility and power. The ability to fine-tune every aspect of the operating system allows for optimal performance in diverse environments.
Furthermore, once users become familiar with navigating through this complexity, they gain a deeper understanding of how their system operates. This knowledge empowers them to customize their Linux experience according to their specific needs and preferences.
In conclusion, the complexity of the Linux kernel should not be dismissed lightly, as it can present challenges for newcomers and casual users. However, with a willingness to learn and access to the wealth of resources available within the Linux community, users can gradually unravel this complexity and harness the true potential of the Linux kernel. Embracing this journey of discovery opens doors to a world of customization, performance optimization, and endless possibilities in the realm of open-source computing.
Limited Support
Exploring a Con of the Linux Kernel: Limited Support
While the Linux kernel boasts numerous advantages, it is important to acknowledge that, like any operating system, it also has its limitations. One such drawback is the limited support available compared to commercial operating systems.
When encountering issues with the Linux kernel, users often rely on online resources and forums for troubleshooting. The open-source nature of Linux fosters a vast community of knowledgeable users who willingly share their expertise and solutions. This community-driven support can be invaluable, especially for experienced users who are comfortable diving into technical details and exploring solutions independently.
However, for those seeking more comprehensive support or assistance from vendors or developers, the options may be more limited compared to commercial operating systems. While there are companies that provide commercial support for specific distributions or customized versions of Linux, the level of support may not match what one would typically expect from a paid service.
This limitation arises from the decentralized nature of Linux development. The Linux kernel is developed collaboratively by a global community of volunteers and organizations who contribute their time and expertise. As a result, there is no centralized entity responsible for providing extensive customer support or troubleshooting assistance.
It is worth noting that some companies do offer enterprise-level support for specific distributions or versions of Linux. These services typically come at a cost and cater to businesses with specific needs or requirements. However, such commercial support may not be as readily available or accessible to individual users or hobbyists.
Nevertheless, it is essential to recognize that despite limited official support channels, the Linux community remains highly active and responsive in addressing issues. Online forums and communities are filled with passionate individuals who freely share their knowledge and assist others facing challenges.
Moreover, the open-source nature of Linux allows users to actively participate in problem-solving by reporting bugs, contributing patches, or even developing their own solutions. This collaborative approach empowers users to take control of their computing experience and find resolutions within the vast ecosystem surrounding Linux.
In conclusion, while the Linux kernel may have limited official support compared to commercial operating systems, it is important to consider the broader context. The active and dedicated Linux community, along with readily available online resources, often compensates for this drawback. By leveraging the collective knowledge and expertise of the community, users can navigate and resolve issues effectively. The spirit of collaboration and self-reliance that defines the Linux ecosystem continues to drive its growth and success despite this con.
Security Vulnerabilities
Addressing Security Vulnerabilities in the Linux Kernel
The Linux kernel, renowned for its robustness and security, is not immune to the presence of vulnerabilities. As with any software, it is essential to acknowledge that security risks can arise within the Linux kernel. However, it is crucial to note that the Linux community has a proactive approach towards identifying and addressing these vulnerabilities promptly.
One of the key strengths of the Linux ecosystem lies in its open-source nature. This means that thousands of developers worldwide actively contribute to its development, reviewing and scrutinizing every line of code. With such a vast pool of expertise, vulnerabilities are often discovered quickly and reported back to the community.
The Linux community takes security seriously and promptly responds to identified vulnerabilities. When a security flaw is detected, developers work diligently to develop patches or updates that address these issues. These patches are then released as updates for users to apply, ensuring that their systems remain secure.
Regular updates play a vital role in maintaining the security of any software system, including the Linux kernel. By keeping their systems up-to-date with the latest patches and fixes, users can mitigate potential risks associated with known vulnerabilities.
To further enhance security measures, various organizations and communities conduct rigorous testing on new kernel releases before they are made available for widespread use. This helps identify any potential weaknesses or security flaws early on in the development process.
Additionally, many distributions provide tools and utilities that make it easier for users to manage updates effectively. These tools streamline the process of applying patches and ensure that critical security updates are not overlooked.
While no software can claim absolute immunity from vulnerabilities, it is important to recognize that the Linux community’s dedication to addressing security concerns sets it apart. The collaborative efforts of developers worldwide result in swift identification and resolution of vulnerabilities within the Linux kernel.
To make the most of this proactive approach towards security, users should remain vigilant about applying updates promptly. Regularly checking for new patches or enabling automatic updates can help ensure that their Linux systems remain secure and protected against potential threats.
In conclusion, while security vulnerabilities can exist within the Linux kernel, the Linux community’s commitment to addressing these issues is commendable. By actively developing patches and updates, and with the support of a vigilant user base, the Linux ecosystem remains resilient against potential security risks. By staying informed and promptly applying updates, users can continue to enjoy the benefits of a secure and reliable operating system.
Compatibility Issues
Navigating Compatibility Issues: A Con of the Linux Kernel
While the Linux kernel is renowned for its stability and versatility, it is not without its challenges. One significant drawback that users may encounter is compatibility issues, particularly when running on newer hardware components or peripherals that have not been thoroughly tested with the version of the Linux kernel in use.
As technology advances at a rapid pace, hardware manufacturers introduce new devices and components to the market. While efforts are made to ensure compatibility with various operating systems, including Linux, there can be instances where certain hardware may not work seamlessly with a specific version of the kernel.
This compatibility gap can lead to frustrations for users who rely on these newer hardware components or peripherals. It may result in limited functionality, reduced performance, or even complete incompatibility. This issue is more prevalent when using older versions of the Linux kernel that have not been updated to include support for the latest hardware advancements.
However, it’s important to note that the Linux community actively works towards addressing these compatibility challenges. Developers continually strive to incorporate support for new hardware into subsequent kernel releases through driver updates and system enhancements. Additionally, many hardware manufacturers collaborate with the open-source community to provide drivers or firmware updates specifically designed for Linux users.
To mitigate compatibility issues, it’s advisable to research and choose hardware components that are known to be compatible with Linux or have a history of good support from manufacturers. Consulting forums and user communities can also provide valuable insights into potential compatibility hurdles and workarounds.
Furthermore, as Linux gains popularity and market share continues to grow, more attention is being given to ensuring broader hardware compatibility right from the development stage. This ongoing effort aims to reduce instances of compatibility issues by proactively incorporating support for a wider range of devices into future releases of the Linux kernel.
In conclusion, while compatibility issues can pose challenges when using certain versions of the Linux kernel with newer hardware components or peripherals, it’s important to recognize that the Linux community is dedicated to addressing these concerns. By staying informed, selecting compatible hardware, and actively participating in the Linux user community, users can navigate these compatibility hurdles and continue to benefit from the stability and versatility that Linux offers.