Enhancing Network Security with Linux Network Security Tools
Linux Network Security Tools: Safeguarding Your Systems
In today’s interconnected world, network security is paramount to protect your systems from cyber threats. Linux, known for its robustness and flexibility, offers a plethora of powerful network security tools that can help you fortify your infrastructure. Let’s explore some essential Linux network security tools that can enhance the security of your networks:
iptables
iptables is a versatile firewall tool that allows you to configure packet filtering rules to control incoming and outgoing network traffic. With iptables, you can set up rules to block malicious traffic, prevent DoS attacks, and secure your network against unauthorized access.
Snort
Snort is an open-source intrusion detection system (IDS) that monitors network traffic in real-time to detect and prevent suspicious activities. It uses rule-based detection mechanisms to identify potential threats and alert system administrators to take appropriate action.
Wireshark
Wireshark is a powerful network protocol analyzer that allows you to capture and inspect the data flowing over your network. By analysing packet captures, you can identify vulnerabilities, troubleshoot network issues, and ensure the integrity of your network communications.
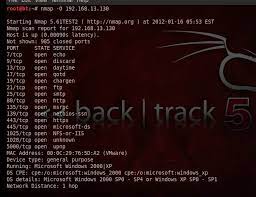
Nmap
Nmap is a versatile network scanning tool that helps you discover hosts and services on your network. With its extensive features, Nmap enables you to identify open ports, detect potential vulnerabilities, and assess the security posture of your systems.
Fail2ban
Fail2ban is a log-parsing tool that scans log files for malicious activity such as repeated login failures or suspicious access patterns. Upon detecting such activities, Fail2ban takes proactive measures like blocking IP addresses to prevent further attacks.
OpenVPN
OpenVPN is a popular open-source VPN solution that enables secure remote access to your network over encrypted tunnels. By using OpenVPN, you can create a secure communication channel for remote users while ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
By leveraging these Linux network security tools along with best practices in cybersecurity, you can strengthen the defences of your networks and safeguard your systems against evolving threats in the digital landscape.
Essential FAQs on Linux Network Security Tools: Understanding Their Role and Best Practices
- What are Linux network security tools?
- How do Linux network security tools help in safeguarding systems?
- Which is the most commonly used firewall tool in Linux for network security?
- What is an intrusion detection system (IDS) in the context of Linux network security tools?
- How can Wireshark assist in enhancing network security on a Linux system?
- What is Nmap and how does it contribute to network security on Linux systems?
- Why is Fail2ban considered a useful tool for enhancing network security on Linux servers?
- What role does OpenVPN play in securing networks on a Linux platform?
- What are some best practices for implementing and managing Linux network security tools effectively?
What are Linux network security tools?
Linux network security tools refer to a diverse range of software applications specifically designed to enhance the security of networks running on Linux operating systems. These tools play a crucial role in safeguarding network infrastructures against cyber threats such as malware, intrusion attempts, and data breaches. From firewall solutions like iptables to intrusion detection systems like Snort and network scanning tools like Nmap, Linux network security tools offer comprehensive protection by allowing users to monitor, analyse, and control network traffic effectively. By leveraging these tools, organisations and individuals can proactively defend their networks, detect vulnerabilities, and maintain the integrity of their digital assets in an increasingly interconnected world.
How do Linux network security tools help in safeguarding systems?
Linux network security tools play a vital role in safeguarding systems by providing robust capabilities to monitor, control, and protect network infrastructure. These tools help in detecting and mitigating potential threats such as malicious traffic, intrusion attempts, and vulnerabilities that could compromise system security. By using tools like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, network scanners, and VPN solutions, Linux users can establish multiple layers of defence to fortify their networks against cyber attacks. Through real-time monitoring, analysis of network traffic, and proactive measures like blocking suspicious activities, Linux network security tools enhance the resilience of systems and contribute to maintaining a secure computing environment.
Which is the most commonly used firewall tool in Linux for network security?
When it comes to network security in Linux, one of the most commonly used firewall tools is iptables. iptables is a powerful and flexible firewall utility that allows users to set up rules for packet filtering, network address translation, and port forwarding. Its robust features make it a popular choice for securing Linux systems by controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic effectively. With iptables, users can configure custom rules to protect their networks from malicious activities and unauthorised access, making it an essential tool for enhancing the security posture of Linux-based systems.
What is an intrusion detection system (IDS) in the context of Linux network security tools?
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) in the context of Linux network security tools is a crucial component that monitors network traffic for suspicious activities or potential security breaches. IDS works by analysing incoming and outgoing data packets, looking for anomalies or patterns that indicate malicious behaviour. When unusual activity is detected, the IDS generates alerts to notify system administrators, enabling them to investigate and respond to potential threats promptly. By deploying an IDS as part of your Linux network security strategy, you can enhance your ability to detect and mitigate cyber threats, bolstering the overall security posture of your systems.
How can Wireshark assist in enhancing network security on a Linux system?
Wireshark plays a crucial role in enhancing network security on a Linux system by providing powerful network protocol analysis capabilities. With Wireshark, administrators can capture and inspect network traffic in real-time, allowing them to identify suspicious activities, potential vulnerabilities, and malicious behaviour. By analysing packet captures with Wireshark, administrators can gain insights into the communication patterns within their network, detect anomalies, and troubleshoot security incidents effectively. Furthermore, Wireshark enables the monitoring of network traffic to ensure compliance with security policies and regulations, making it an indispensable tool for enhancing the overall security posture of a Linux system.
What is Nmap and how does it contribute to network security on Linux systems?
Nmap, short for “Network Mapper,” is a powerful network scanning tool widely used in the realm of cybersecurity on Linux systems. It serves as a versatile utility that allows system administrators and security professionals to discover hosts, services, and open ports on a network. By providing detailed information about network assets, Nmap enables users to conduct security assessments, identify potential vulnerabilities, and assess the overall security posture of their systems. With its comprehensive features and robust scanning capabilities, Nmap plays a crucial role in enhancing network security on Linux systems by empowering users to proactively monitor and protect their networks against cyber threats.
Why is Fail2ban considered a useful tool for enhancing network security on Linux servers?
Fail2ban is widely regarded as a valuable tool for bolstering network security on Linux servers due to its proactive approach in mitigating potential threats. By monitoring log files for suspicious activities such as repeated login failures or unusual access patterns, Fail2ban can swiftly identify and respond to malicious behaviour. Through its automated blocking of IP addresses associated with such activities, Fail2ban helps prevent brute-force attacks, unauthorized access attempts, and other security breaches. This capability not only enhances the overall security posture of Linux servers but also reduces the risk of successful cyber attacks, making Fail2ban an indispensable tool for safeguarding networks against evolving threats.
What role does OpenVPN play in securing networks on a Linux platform?
OpenVPN plays a crucial role in securing networks on a Linux platform by providing a robust and reliable Virtual Private Network (VPN) solution. As an open-source software, OpenVPN enables users to create encrypted tunnels for secure communication over public networks, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity. By utilising OpenVPN on Linux, organisations can establish secure connections for remote access, site-to-site connectivity, and data encryption, thereby enhancing network security and protecting sensitive information from potential threats. Its flexibility, ease of deployment, and strong encryption capabilities make OpenVPN an essential tool for safeguarding networks on a Linux platform.
What are some best practices for implementing and managing Linux network security tools effectively?
When it comes to implementing and managing Linux network security tools effectively, there are several best practices that can help enhance the overall security posture of your systems. Firstly, it is crucial to regularly update and patch your network security tools to ensure they are equipped to defend against the latest threats. Additionally, configuring firewall rules and access controls based on the principle of least privilege can minimise the attack surface and restrict unauthorised access. Monitoring network traffic using intrusion detection systems like Snort and analysing packet captures with Wireshark can help identify potential threats early on. Implementing strong authentication mechanisms, conducting regular security audits, and educating users about cybersecurity best practices are also essential steps in maintaining a robust network security framework on Linux systems.