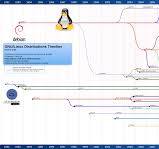
The Evolution of Linux Distributions: A Timeline
The Evolution of Linux Distributions: A Timeline
Linux distributions, or distros, have a rich history that dates back to the early days of the open-source movement. Let’s take a journey through time to explore the evolution of Linux distros and how they have shaped the computing landscape.
1991 – 1995: The Birth of Linux
In 1991, Linus Torvalds released the first version of the Linux kernel. This event marked the beginning of a new era in computing, as developers around the world started to build their own operating systems based on this kernel.
1993: Slackware and Debian
Slackware and Debian were among the first Linux distributions to be developed. Slackware focused on simplicity and stability, while Debian emphasised free software principles and package management.
1994: Red Hat Linux
Red Hat Linux was founded in 1994 and quickly gained popularity for its user-friendly approach and support for enterprise users. It laid the foundation for future enterprise-focused distributions.
Late 1990s: Rise of Ubuntu and Fedora
In the late 1990s, Ubuntu and Fedora emerged as prominent players in the Linux distribution scene. Ubuntu aimed to provide a user-friendly experience for desktop users, while Fedora focused on innovation and cutting-edge technologies.
2000s: Diversity and Specialisation
During the 2000s, we saw an explosion of new distributions catering to various niches and user preferences. Distributions like Arch Linux, CentOS, and openSUSE gained popularity for their unique features and target audiences.
Present Day: Continual Innovation
Today, the world of Linux distributions continues to evolve with a focus on security, performance, and usability. Distros like Ubuntu LTS, Fedora Workstation, and CentOS Stream are leading the way in providing reliable solutions for users across different domains.
Tracing the Evolution of Linux: Key Milestones in Distribution Development
- In 1991, the first Linux distribution, MCC Interim Linux, was released.
- Slackware, one of the earliest and still actively maintained distributions, was launched in 1993.
- Debian, known for its stability and package management system, debuted in 1993.
- Red Hat Linux emerged in 1994 and later evolved into Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL).
- Ubuntu, a popular user-friendly distribution based on Debian, was introduced in 2004.
- Arch Linux is a minimalist distribution founded in 2002 that follows a rolling release model.
- Linux Mint gained popularity for its ease of use and multimedia support since its launch in 2006.
- Fedora is a community-driven distribution sponsored by Red Hat that has been around since 2003.
In 1991, the first Linux distribution, MCC Interim Linux, was released.
In 1991, a significant milestone in the history of Linux distributions was reached with the release of the first-ever distribution, MCC Interim Linux. This event marked the beginning of a new era in computing, as it paved the way for the development of numerous other distributions that would follow. MCC Interim Linux set the foundation for what would become a diverse and thriving ecosystem of Linux operating systems, each with its own unique features and contributions to the open-source community.
Slackware, one of the earliest and still actively maintained distributions, was launched in 1993.
One of the pioneering Linux distributions, Slackware, made its debut in 1993 and continues to be actively maintained to this day. Known for its focus on simplicity and stability, Slackware has stood the test of time as one of the longest-running distributions in the open-source community. Its enduring presence highlights its enduring appeal to users seeking a reliable and straightforward Linux experience.
Debian, known for its stability and package management system, debuted in 1993.
Debian, renowned for its exceptional stability and robust package management system, made its debut in 1993. Since its inception, Debian has been a cornerstone in the world of Linux distributions, attracting users and developers alike with its commitment to free software principles and reliable performance. With a strong focus on security and ease of use, Debian has established itself as a trusted choice for those seeking a dependable operating system that stands the test of time.
Red Hat Linux emerged in 1994 and later evolved into Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL).
In 1994, Red Hat Linux made its debut in the Linux distribution landscape, quickly gaining recognition for its user-friendly interface and robust features. Over time, Red Hat Linux underwent a transformation, evolving into Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). This shift towards enterprise-focused solutions solidified Red Hat’s position as a key player in the industry, offering businesses a secure and reliable operating system backed by professional support and services.
Ubuntu, a popular user-friendly distribution based on Debian, was introduced in 2004.
In 2004, Ubuntu was introduced as a popular user-friendly Linux distribution based on Debian. Known for its ease of use and comprehensive software ecosystem, Ubuntu quickly gained widespread adoption among both novice and experienced users. With regular updates and long-term support releases, Ubuntu has become a go-to choice for individuals and organisations seeking a reliable and user-centric operating system built on the solid foundation of Debian.
Arch Linux is a minimalist distribution founded in 2002 that follows a rolling release model.
Arch Linux, established in 2002, is a minimalist distribution renowned for its simplicity and flexibility. Embracing a rolling release model, Arch Linux provides users with the latest software updates continuously, ensuring a cutting-edge computing experience. This approach allows users to have greater control over their system’s components and configurations, making Arch Linux a popular choice among advanced users and enthusiasts seeking a highly customisable operating system.
Linux Mint gained popularity for its ease of use and multimedia support since its launch in 2006.
Since its launch in 2006, Linux Mint has garnered widespread acclaim for its user-friendly interface and robust multimedia support. The distribution’s focus on simplicity and seamless out-of-the-box experience has attracted a large user base seeking a reliable and intuitive operating system. With its emphasis on usability and multimedia capabilities, Linux Mint has established itself as a popular choice among both novice and experienced users in the Linux community.
Fedora is a community-driven distribution sponsored by Red Hat that has been around since 2003.
Fedora, a community-driven distribution sponsored by Red Hat, has been a significant player in the Linux ecosystem since its inception in 2003. Known for its commitment to innovation and cutting-edge technologies, Fedora has attracted a dedicated community of developers and users who contribute to its continual evolution and improvement. With strong support from Red Hat, Fedora remains at the forefront of providing a reliable and feature-rich operating system for enthusiasts and professionals alike.