PCLinuxOS: Empowering Users with a User-Friendly Linux Experience
In the vast landscape of Linux distributions, PCLinuxOS stands out as a user-friendly operating system that focuses on simplicity, stability, and accessibility. With its roots dating back to 2003, PCLinuxOS has evolved into a mature and reliable distribution that caters to both newcomers and experienced Linux users alike.
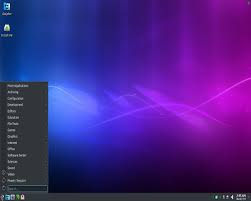
User-Friendly Interface
One of the key strengths of PCLinuxOS lies in its intuitive interface. The developers have carefully crafted a desktop environment that is easy to navigate, making it an ideal choice for those transitioning from other operating systems. Whether you prefer the traditional KDE Plasma desktop or the lightweight Xfce environment, PCLinuxOS provides a familiar and comfortable experience.
Software Management Made Easy
Installing and managing software on PCLinuxOS is a breeze thanks to its user-friendly package management system. The distribution utilizes Synaptic Package Manager, which allows users to effortlessly search for and install applications from an extensive software repository. Additionally, with the APT-RPM package management tool, updating your system and keeping it secure becomes a seamless process.
Stability and Reliability
PCLinuxOS prides itself on providing a stable and reliable operating system. Its development team rigorously tests updates before releasing them to ensure compatibility and minimize any potential issues. This commitment to stability ensures that users can rely on their systems without worrying about unexpected crashes or glitches.
Vibrant Community Support
Behind every successful distribution is a vibrant community, and PCLinuxOS is no exception. The community surrounding PCLinuxOS is known for its friendliness and willingness to help users with any questions or issues they may encounter. Online forums, mailing lists, and chat channels provide ample opportunities for users to connect with fellow enthusiasts, share knowledge, troubleshoot problems together, or simply engage in friendly discussions.
Customization Options Galore
One of the hallmarks of Linux is its flexibility, and PCLinuxOS embraces this philosophy by offering a wide range of customization options. Users can personalize their desktop environments, tweak system settings, and choose from a variety of pre-installed software packages to suit their specific needs. This level of customization empowers users to create an environment that truly reflects their preferences and workflow.
Conclusion
PCLinuxOS has carved out a niche for itself in the Linux world by prioritizing user-friendliness, stability, and accessibility. With its intuitive interface, easy software management, and strong community support, PCLinuxOS provides a welcoming environment for newcomers while still catering to the needs of experienced Linux users. Whether you are looking to explore the world of Linux or seeking a reliable operating system for your daily tasks, PCLinuxOS is worth considering as it continues to empower users with its user-friendly approach.
7 Essential Tips for Getting the Most Out of PCLinuxOS
- Make sure to keep your PCLinuxOS system up-to-date by running the Update Manager regularly.
- Use the Synaptic Package Manager to install and remove packages easily.
- Use the MyLiveCD utility to create a bootable USB drive or CD/DVD with PCLinuxOS installed on it in case of emergency.
- Take advantage of PCLinuxOS’s wide range of available applications, such as LibreOffice, GIMP, and Firefox, which can be found in the Software Repositories.
- Learn about how to customize your desktop environment with KDE Control Center and other tools available in PCLinuxOS for a more personalised experience.
- Join the friendly community on IRC or their forums for help and support if you have any issues with your system or need advice about specific topics related to PCLinuxOS usage and development
- Make use of the many tutorials available online that will help you get started with using PCLinuxOS quickly and easily!
Make sure to keep your PCLinuxOS system up-to-date by running the Update Manager regularly.
Keeping Your PCLinuxOS System Secure: The Importance of Regular Updates
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, staying up-to-date is crucial to ensure the security and optimal performance of your system. This holds true for PCLinuxOS, a user-friendly Linux distribution that prioritizes stability and reliability. To make the most out of your PCLinuxOS experience, it is essential to regularly run the Update Manager and keep your system up-to-date.
Why Are Updates Important?
Updates play a vital role in maintaining the security and stability of your PCLinuxOS system. Software vulnerabilities can be discovered over time, and updates often contain patches that address these vulnerabilities. By regularly updating your system, you ensure that any potential security flaws are promptly addressed, reducing the risk of malware infections or unauthorized access to your data.
Furthermore, updates bring improvements in performance and functionality. Developers continually work on refining their software, fixing bugs, and introducing new features. By keeping your system up-to-date, you can benefit from these enhancements and enjoy a smoother and more efficient computing experience.
Using the Update Manager
PCLinuxOS simplifies the process of updating your system through its dedicated tool called Update Manager. This user-friendly utility allows you to effortlessly manage updates with just a few clicks.
To access the Update Manager, simply navigate to the system menu or panel on your desktop environment and locate the relevant icon or entry. Launching the Update Manager will initiate a scan for available updates for both the operating system itself and installed software packages.
Once the scan is complete, you will be presented with a list of available updates categorized by their importance level (such as security updates or general software updates). You can review these updates and select which ones you wish to install. It is generally recommended to install all available updates to ensure comprehensive coverage for security patches and overall system improvements.
After making your selection, click on the “Apply” or “Install” button to initiate the update process. The Update Manager will handle the rest, downloading and installing the selected updates onto your system.
Make it a Habit
To ensure that your PCLinuxOS system remains secure and up-to-date, it is advisable to make running the Update Manager a regular habit. Set a reminder to check for updates weekly or monthly, depending on your preference and usage patterns. By doing so, you can stay ahead of potential security risks and enjoy the latest enhancements that PCLinuxOS has to offer.
Conclusion
Regularly running the Update Manager in PCLinuxOS is a simple yet essential practice to maintain the security and optimal performance of your system. By keeping your operating system and software packages up-to-date, you minimize security vulnerabilities, benefit from performance improvements, and ensure a smoother computing experience overall. Embrace this good habit and make it a priority to safeguard your PCLinuxOS system by staying updated with the latest patches and enhancements.
Use the Synaptic Package Manager to install and remove packages easily.
PCLinuxOS Tip: Simplify Package Management with Synaptic Package Manager
Managing software packages is a fundamental aspect of any operating system, and PCLinuxOS offers a convenient solution with its Synaptic Package Manager. Whether you’re new to Linux or a seasoned user, utilizing this powerful tool can greatly simplify the process of installing and removing packages on your PCLinuxOS system.
Synaptic Package Manager provides an intuitive graphical interface that allows users to browse through an extensive software repository. With just a few clicks, you can search for specific applications or explore different categories to discover new software. This user-friendly approach makes it easy for both beginners and experienced users to find the packages they need.
Installing packages using Synaptic is a straightforward process. Once you’ve located the desired package, simply select it and click on the “Apply” button. Synaptic will handle all the necessary dependencies automatically, ensuring that your chosen package is installed correctly without any hassle.
Similarly, removing unwanted packages is just as effortless. By selecting the package you wish to remove and clicking on “Apply,” Synaptic will take care of uninstalling it from your system along with any associated files or dependencies. This streamlined approach saves time and eliminates the need for manual cleanup after removing packages.
Furthermore, Synaptic allows you to manage updates effectively. It provides an overview of available updates for installed packages, making it easy to keep your system up-to-date with the latest security patches and bug fixes. With just a few clicks, you can update multiple packages simultaneously, ensuring that your PCLinuxOS system remains secure and optimized.
The benefits of using Synaptic Package Manager extend beyond its user-friendly interface. Behind the scenes, it leverages APT-RPM, a robust package management tool known for its reliability and efficiency. APT-RPM ensures seamless integration between Synaptic and PCLinuxOS’s underlying system components, guaranteeing smooth operations during package installations or removals.
Whether you’re a software enthusiast looking to explore new applications or a business professional seeking essential tools, PCLinuxOS’s Synaptic Package Manager simplifies the entire process. With its intuitive interface, automatic dependency handling, and efficient package management capabilities, Synaptic empowers users to install, update, and remove packages effortlessly.
Take advantage of this handy tip and discover the convenience of Synaptic Package Manager on your PCLinuxOS system. Enjoy a streamlined package management experience that saves time and enhances your overall Linux journey.
Use the MyLiveCD utility to create a bootable USB drive or CD/DVD with PCLinuxOS installed on it in case of emergency.
PCLinuxOS Tip: Create a Bootable USB Drive or CD/DVD with MyLiveCD Utility
In the world of technology, emergencies can happen when we least expect them. Whether it’s a sudden system crash, hardware failure, or the need to access your files on another computer, having a backup plan in place is crucial. PCLinuxOS offers a handy tool called MyLiveCD that allows you to create a bootable USB drive or CD/DVD with PCLinuxOS installed on it, providing you with a lifeline in times of need.
The MyLiveCD utility is designed to simplify the process of creating a portable version of PCLinuxOS that you can carry with you wherever you go. This means that even if your main computer experiences issues, you can still boot into PCLinuxOS using the USB drive or CD/DVD and have access to your files and essential applications.
Creating a bootable USB drive or CD/DVD using MyLiveCD is straightforward. Here’s how:
- Launch the MyLiveCD utility from the PCLinuxOS menu.
- Follow the step-by-step instructions provided by the utility.
- Select the desired options, such as language preferences and software packages to include.
- Choose whether you want to create a bootable USB drive or burn the image onto a CD/DVD.
- Insert your USB drive or blank CD/DVD into your computer.
- Let MyLiveCD do its magic – it will automatically create an image of PCLinuxOS and install it onto your chosen media.
Once the process is complete, you’ll have your very own portable version of PCLinuxOS ready to use in case of emergencies. To boot into this portable version, simply insert the USB drive or CD/DVD into any compatible computer and restart it.
Having this backup solution at hand ensures that you’re never caught off guard when facing unexpected situations. Whether you need to retrieve important documents, access specific applications, or troubleshoot issues on another machine, the bootable USB drive or CD/DVD created with MyLiveCD will come to your rescue.
Remember to periodically update your backup media with the latest version of PCLinuxOS to ensure you have access to the most recent features and security updates.
In conclusion, the MyLiveCD utility in PCLinuxOS is a valuable tool that empowers users to create a portable version of their operating system for emergency situations. By having a bootable USB drive or CD/DVD with PCLinuxOS installed, you can confidently tackle unexpected challenges and ensure your data and productivity remain intact.
Take advantage of PCLinuxOS’s wide range of available applications, such as LibreOffice, GIMP, and Firefox, which can be found in the Software Repositories.
Unlocking the Power of PCLinuxOS: Exploring a Wealth of Applications
PCLinuxOS, a user-friendly Linux distribution, offers an impressive array of applications that cater to various needs and interests. By taking advantage of the software repositories, users can easily access popular applications like LibreOffice, GIMP, and Firefox, among many others. Let’s dive into how these applications enhance the PCLinuxOS experience.
LibreOffice: Unleash Your Productivity
PCLinuxOS brings LibreOffice, a powerful and feature-rich office suite, right at your fingertips. With LibreOffice Writer, you can create professional documents; Calc enables you to handle spreadsheets with ease; Impress empowers you to craft stunning presentations; and Draw allows for intuitive graphic editing. Whether for work or personal projects, LibreOffice equips you with the tools needed to boost productivity.
GIMP: Unleash Your Creativity
If unleashing your artistic side is on your agenda, PCLinuxOS offers GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program). This robust image editing software is perfect for graphic designers, photographers, or anyone looking to enhance their visual creations. With GIMP’s extensive features and tools, you can retouch photos, create digital artworks, design logos, and much more.
Firefox: Unleash Your Browsing Experience
PCLinuxOS provides Firefox as its default web browser. Firefox is renowned for its speed, security features, and customizability. Enjoy a smooth browsing experience while exploring the vast expanse of the internet. With Firefox’s add-ons and extensions ecosystem at your disposal, you can tailor your browsing experience according to your preferences.
Software Repositories: A Treasure Trove of Possibilities
The Software Repositories in PCLinuxOS act as a treasure trove of applications waiting to be discovered. These repositories contain an extensive collection of software packages that cover a wide range of categories such as multimedia, graphics, development tools, utilities, and more. Simply browse the repositories using the user-friendly Synaptic Package Manager or APT-RPM tool to find the applications that suit your needs.
Embrace the PCLinuxOS Experience
PCLinuxOS empowers users with its wide range of available applications. Whether you need office productivity tools, creative software for image editing, or a reliable web browser, PCLinuxOS has you covered. Explore the Software Repositories and unlock a world of possibilities.
With PCLinuxOS’s commitment to user-friendliness and stability, combined with its vibrant community support, you can enjoy a seamless and enriching Linux experience. So go ahead, take advantage of the vast selection of applications and unleash your full potential with PCLinuxOS!
Customize Your PCLinuxOS Desktop: Personalize Your Linux Experience
PCLinuxOS offers a plethora of customization options to tailor your desktop environment to your liking, allowing you to create a truly personalized Linux experience. With tools like the KDE Control Center and other available utilities, you can easily tweak various aspects of your desktop, making it uniquely yours.
One of the standout features of PCLinuxOS is its integration with the KDE Plasma desktop environment. KDE is renowned for its flexibility and extensive customization capabilities. To harness the full potential of this powerful desktop environment, you can utilize the KDE Control Center.
The KDE Control Center serves as a central hub for customizing various aspects of your desktop. From changing themes and wallpapers to configuring window behavior and appearance, this tool puts you in full control. You can easily access it through the system settings menu or by right-clicking on the desktop and selecting “Configure Desktop.”
Within the KDE Control Center, you’ll find a range of options to personalize your desktop environment. You can choose from a variety of pre-installed themes or download new ones from online repositories to change the overall look and feel of your system. Additionally, you can customize icons, fonts, colours, and even mouse cursor styles to match your preferences.
But customization doesn’t stop at aesthetics alone. The KDE Control Center also allows you to fine-tune system settings for optimal performance and usability. You can adjust power management settings to optimize energy consumption or configure input devices such as keyboards and mice according to your preferences.
Apart from the KDE Control Center, PCLinuxOS offers additional tools that further enhance customization possibilities. For instance, KWin Window Manager enables you to tweak window behavior, including window decorations, effects, and shortcuts. With this tool, you can define how windows behave when moved or resized or even enable eye-catching visual effects.
Moreover, PCLinuxOS provides an array of widgets that you can add to your desktop. These widgets range from weather and clock displays to system monitors and application launchers, allowing you to create a personalized dashboard tailored to your needs.
By taking advantage of the customization options available in PCLinuxOS, you can transform your desktop environment into a reflection of your style and workflow. Whether you prefer a sleek and minimalistic look or a vibrant and dynamic interface, PCLinuxOS empowers you to make it happen.
So, dive into the world of customization with PCLinuxOS, explore the KDE Control Center, experiment with themes, icons, and widgets, and create a desktop environment that truly suits your personality and enhances your Linux experience.
Join the PCLinuxOS Community: Get Help and Support from a Friendly Network
When it comes to using an operating system like PCLinuxOS, having a supportive community by your side can make all the difference. Whether you encounter technical issues or simply want to seek advice on specific topics related to PCLinuxOS usage and development, joining the friendly community on IRC or their forums is a valuable resource.
The PCLinuxOS community is known for its welcoming atmosphere and willingness to assist users of all levels of expertise. By connecting with fellow enthusiasts, you gain access to a wealth of knowledge and experience that can help you overcome any obstacles you may encounter along your Linux journey.
IRC (Internet Relay Chat) provides real-time communication with other users who are passionate about PCLinuxOS. Joining an IRC channel dedicated to PCLinuxOS allows you to engage in live discussions, ask questions, and receive immediate assistance. The interactive nature of IRC creates an environment where you can connect with like-minded individuals who share your enthusiasm for this powerful operating system.
Additionally, the PCLinuxOS forums offer another avenue for seeking help and support. These online discussion boards provide a platform for users to connect, share experiences, and exchange information about various aspects of using and developing PCLinuxOS. Whether you have questions about software installation, system configuration, or general troubleshooting, posting on the forums ensures that your queries reach a wide audience who are eager to assist.
By actively participating in these community spaces, you not only gain valuable insights into using PCLinuxOS but also contribute to the growth and development of the distribution itself. Sharing your experiences, offering solutions to others’ problems, or even suggesting improvements helps foster collaboration within the community.
Remember that joining these communities is not just about seeking help; it’s also an opportunity to forge friendships with individuals who share your passion for Linux. Engaging in discussions beyond technical support can lead to discovering new ideas, projects, and even lifelong connections with like-minded individuals.
So, if you find yourself facing any challenges or simply want to connect with others who appreciate PCLinuxOS, don’t hesitate to join the friendly community on IRC or their forums. Embrace the power of collective knowledge and experience, and let the PCLinuxOS community guide you towards a successful and enjoyable Linux journey.
Make use of the many tutorials available online that will help you get started with using PCLinuxOS quickly and easily!
Unlock the Power of PCLinuxOS with Online Tutorials
Embarking on a new operating system can be an exciting but daunting experience. Thankfully, if you’re venturing into the world of PCLinuxOS, there’s a wealth of online tutorials available to help you navigate through its features and get up to speed quickly and effortlessly.
PCLinuxOS is known for its user-friendly approach, but even the most intuitive systems can benefit from a little guidance. Whether you’re a Linux novice or an experienced user seeking to explore PCLinuxOS’s unique offerings, these tutorials are invaluable resources that will pave your way to success.
The internet is teeming with dedicated communities, passionate individuals, and knowledgeable experts who have taken the time to create comprehensive tutorials covering various aspects of PCLinuxOS. From installation guides to desktop customization tips, software management tricks to troubleshooting techniques, these tutorials cater to users of all skill levels.
By making use of these online resources, you can unlock the full potential of PCLinuxOS in no time. Here’s how:
- Start with the Basics: If you’re new to PCLinuxOS or Linux in general, begin with beginner-friendly tutorials that introduce you to the fundamentals. These guides will walk you through essential concepts such as navigating the desktop environment, managing files and folders, and understanding key terminologies.
- Dive into Software Management: Discover how to install and update software packages using PCLinuxOS’s package management tools. Online tutorials provide step-by-step instructions on using Synaptic Package Manager or APT-RPM effectively. You’ll learn how to explore software repositories, search for specific applications, and keep your system up-to-date with ease.
- Explore Customization Options: One of the great advantages of PCLinuxOS is its flexibility for customization. Online tutorials offer insights into personalizing your desktop environment by adjusting themes, icons, wallpapers, and more. Unleash your creativity and make PCLinuxOS truly your own.
- Troubleshooting Made Easy: Even the smoothest systems encounter occasional hiccups. When faced with challenges, online tutorials can be a lifesaver. Learn how to troubleshoot common issues, find solutions to error messages, and seek guidance on forums or chat channels where the PCLinuxOS community is always ready to help.
Remember, these tutorials are not only for beginners but also for anyone seeking to enhance their PCLinuxOS experience. The vast collection of online resources ensures that you can continuously expand your knowledge and skills as you delve deeper into the operating system.
So, don’t hesitate to take advantage of the many tutorials available online. They’re an invaluable asset that will empower you to unlock the true potential of PCLinuxOS quickly and easily. Embrace the power of knowledge and embark on an exciting journey with PCLinuxOS today!