Unlocking Success: Real Estate CRM Revolutionizing Property Management
The Power of Real Estate CRM in Managing Your Property Business
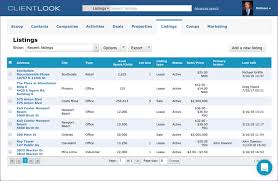
In the competitive world of real estate, managing properties efficiently and effectively is crucial for success. This is where Real Estate Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems come into play. A Real Estate CRM is a powerful tool that helps property professionals streamline their operations, improve customer relationships, and boost productivity.
Benefits of Real Estate CRM:
- Centralised Data Management: A CRM system allows you to store all property-related information in one centralised database, making it easy to access and update property details, client information, and communication logs.
- Improved Customer Relationships: By tracking client interactions, preferences, and feedback, a CRM system enables you to provide personalised services and build stronger relationships with your clients.
- Automated Workflows: Streamline your processes with automated workflows for tasks such as lead management, property listings, follow-ups, and marketing campaigns. This saves time and ensures nothing falls through the cracks.
- Data Analysis: Real-time analytics and reporting features help you track key performance metrics, identify trends, and make informed decisions to optimise your business strategies.
- Enhanced Communication: Stay connected with clients through integrated communication tools like email templates, SMS alerts, and reminders. Keep everyone in the loop with seamless communication channels.
Choosing the Right Real Estate CRM
When selecting a Real Estate CRM for your property business, consider factors such as scalability, customisation options, ease of use, integration capabilities with other software tools (such as property portals), security features, and ongoing support from the provider.
Investing in a reliable Real Estate CRM can transform how you manage your properties, streamline operations, boost sales efficiency, and ultimately drive growth for your real estate business. Embrace the power of technology to stay ahead in the competitive property market!
7 Advantages of Real Estate CRM: Streamlined Management and Enhanced Customer Engagement
- Centralised data management for easy access and updates
- Improved customer relationships through personalised services
- Automated workflows save time and prevent tasks from falling through the cracks
- Real-time analytics and reporting for informed decision-making
- Enhanced communication with integrated tools like email templates and SMS alerts
- Increased efficiency in lead management, property listings, and marketing campaigns
- Scalability, customisation options, and integration capabilities for tailored solutions
Challenges of Real Estate CRM: Cost, Complexity, Security, and Integration Issues
Centralised data management for easy access and updates
Centralised data management is a key advantage of Real Estate CRM systems, offering property professionals a convenient and efficient way to access and update property-related information. By consolidating all data into a centralised database, users can easily retrieve details on properties, client information, communication logs, and more with just a few clicks. This streamlined approach not only saves time but also ensures that information is consistently up-to-date and readily available whenever needed, enhancing overall productivity and organisational efficiency in managing real estate operations.
Improved customer relationships through personalised services
Enhancing customer relationships through personalised services is a key advantage of implementing a Real Estate CRM system. By leveraging client data and interactions stored in the CRM database, property professionals can tailor their services to meet the specific needs and preferences of each client. This personalised approach not only fosters stronger connections with clients but also increases satisfaction levels and loyalty. By delivering targeted and relevant communications, property businesses can build trust, establish long-term relationships, and ultimately drive success in the competitive real estate market.
Automated workflows save time and prevent tasks from falling through the cracks
One significant advantage of implementing a Real Estate CRM system is the ability to utilise automated workflows, which not only save valuable time but also prevent essential tasks from slipping through the cracks. By automating processes such as lead management, property listings, follow-ups, and marketing campaigns, real estate professionals can ensure that every step of the workflow is efficiently executed without manual intervention. This feature not only enhances productivity but also contributes to a more organised and streamlined approach to managing properties and client relationships.
Real-time analytics and reporting for informed decision-making
Real-time analytics and reporting provided by Real Estate CRM systems empower property professionals to make informed decisions based on accurate data and insights. By having access to up-to-date information on key performance metrics, market trends, client preferences, and property listings, real estate agents can strategize effectively, identify opportunities for growth, and adapt their business tactics promptly. This pro of Real Estate CRM not only enhances decision-making processes but also enables businesses to stay agile and competitive in the dynamic real estate industry.
Enhanced communication with integrated tools like email templates and SMS alerts
Enhanced communication is a key advantage of using Real Estate CRM systems, offering integrated tools such as email templates and SMS alerts. These features enable property professionals to maintain seamless and efficient communication with clients, prospects, and team members. By utilising pre-designed email templates, users can send consistent and professional messages to different stakeholders, saving time and ensuring a cohesive brand image. Additionally, SMS alerts provide instant notifications for important updates or reminders, ensuring timely communication that enhances customer engagement and satisfaction. The integrated communication tools in Real Estate CRM systems play a vital role in fostering stronger relationships and improving overall operational efficiency in the property business.
Increased efficiency in lead management, property listings, and marketing campaigns
Real Estate CRM systems offer a significant advantage in improving efficiency across various aspects of property management. One key benefit is the enhanced efficiency in lead management, property listings, and marketing campaigns. By utilising a CRM system, real estate professionals can streamline lead tracking, manage property listings more effectively, and create targeted marketing campaigns with ease. This increased efficiency not only saves time but also ensures that no potential leads are overlooked, properties are showcased optimally, and marketing efforts are targeted towards the right audience for maximum impact. Ultimately, this improved efficiency leads to better productivity and increased success in the competitive real estate market.
Scalability, customisation options, and integration capabilities for tailored solutions
One of the key advantages of Real Estate CRM systems is their scalability, customisation options, and integration capabilities, which allow property professionals to tailor solutions to meet their specific needs. Scalability ensures that the CRM can grow with your business, accommodating changes in property portfolios and expanding client bases. Customisation options enable users to adapt the CRM to align with their unique workflows and business processes. Additionally, integration capabilities with other software tools provide a seamless experience, allowing for efficient data sharing and enhancing overall productivity. This versatility empowers real estate professionals to create tailored solutions that optimise operations and drive success in the dynamic property market.
Costly Investment
Implementing a Real Estate CRM system can pose a notable challenge due to the significant financial investment required, which may be particularly daunting for small businesses or individual agents operating on limited budgets. The initial costs associated with purchasing and setting up the CRM software, as well as ongoing expenses for maintenance, training, and upgrades, can strain financial resources and impact profitability in the short term. Careful consideration and financial planning are essential to weigh the benefits against the costs before committing to integrating a Real Estate CRM system into your property business operations.
Steep Learning Curve
One significant drawback of Real Estate CRM systems is the steep learning curve that users may face. The complexity of the software can present challenges in terms of adaptation, necessitating dedicated time and training to grasp and utilise its full range of features effectively. This learning curve can lead to initial frustrations and potential productivity setbacks as users navigate through the system’s functionalities. However, with patience, perseverance, and proper training, users can overcome this hurdle and harness the benefits that Real Estate CRM systems offer for managing properties efficiently.
Data Security Risks
Data Security Risks are a significant concern when it comes to Real Estate CRM systems. Storing sensitive client information on a CRM platform can expose the data to potential security vulnerabilities if adequate safeguards are not in place. Without proper encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, there is a risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, or theft of confidential information. Real estate professionals must be vigilant in ensuring that their CRM systems have robust security measures in place to protect client data and maintain trust in their business operations.
Integration Challenges
One significant drawback of Real Estate CRM systems is the integration challenges they pose. Compatibility issues with existing systems or the complexity of integrating third-party tools can impede the smooth operation of a Real Estate CRM. These challenges may lead to data silos, inefficiencies in workflow, and potential disruptions in communication between different platforms. Overcoming these integration hurdles requires careful planning, technical expertise, and sometimes additional resources, which can be a barrier for real estate professionals looking to adopt a CRM solution seamlessly into their existing processes.