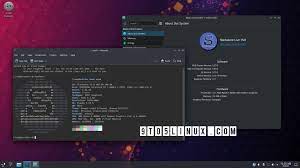
Knoppix: The Pioneering Live Linux Distribution
In the world of Linux distributions, Knoppix stands out as a true pioneer. Developed by Klaus Knopper, a German computer scientist, Knoppix introduced the concept of a live Linux distribution to the masses. With its innovative approach and user-friendly design, Knoppix has become a go-to choice for both beginners and experienced Linux enthusiasts.
What sets Knoppix apart is its ability to run directly from a CD or USB drive without the need for installation on a hard drive. This means that users can experience the power and versatility of Linux without making any changes to their existing system. It’s like having a portable operating system that you can carry with you wherever you go.
One of the key advantages of using Knoppix is its versatility. It comes bundled with an extensive range of software applications, making it suitable for various purposes such as data recovery, system administration, educational use, or just exploring the world of Linux. Whether you’re a student needing to access specific tools for your coursework or an IT professional troubleshooting systems on the go, Knoppix has got you covered.
Another noteworthy feature of Knoppix is its hardware detection capabilities. It excels at automatically recognizing and configuring hardware components, ensuring that most devices work out-of-the-box without any additional configuration required. This makes it an ideal choice for those who want to quickly assess hardware compatibility or diagnose issues with their systems.
Knoppix also places great emphasis on user-friendliness. Its intuitive graphical user interface (GUI) provides easy access to all essential functions and applications while maintaining a familiar look and feel for Windows users transitioning to Linux. Additionally, comprehensive documentation and support resources are available online, making it easier for users to get started and find solutions to any questions they may have.
Over the years, Knoppix has gained immense popularity within the open-source community and beyond. Its influence can be seen in the development of other live Linux distributions that have followed in its footsteps. Many users have found Knoppix to be a reliable and trustworthy tool, especially in critical situations where data recovery or system rescue is required.
Knoppix continues to evolve with regular updates and new releases, ensuring that it stays relevant and up-to-date with the latest advancements in the Linux ecosystem. Its commitment to providing a stable and feature-rich environment has garnered it a loyal following of users who appreciate its reliability and ease of use.
In conclusion, Knoppix remains an outstanding example of innovation and usability in the world of Linux distributions. Its pioneering approach to live Linux has revolutionized the way people interact with this powerful operating system. Whether you’re a novice user looking to dip your toes into the world of Linux or an experienced professional needing a versatile tool, Knoppix is undoubtedly worth exploring. Give it a try, and you may find yourself joining the ranks of those who appreciate its flexibility, reliability, and user-friendly nature.
7 Advantages of Knoppix: A Comprehensive Overview of this Free and Versatile Operating System
- Knoppix is a free and open-source operating system that can be used without installation.
- It can run on almost any computer, making it ideal for rescuing data from an old or damaged hard drive.
- Knoppix includes a wide range of applications and tools, so you don’t need to install additional software to get started.
- It provides good security features, such as encryption and secure booting options, making it suitable for sensitive tasks like online banking or storing confidential files.
- It has excellent hardware detection capabilities, so it works well with older hardware components that may not be supported by newer operating systems.
- The graphical user interface is easy to use and navigate, even for beginners who are unfamiliar with Linux-based systems .
- Knoppix comes with plenty of documentation and tutorials which makes learning how to use the OS easier than ever before!
Limitations and Challenges of Knoppix: A Comprehensive Overview for UK Users
- Knoppix is not compatible with all hardware, which may limit its usefulness.
- Knoppix does not come with any technical support, so users must find their own solutions to any problems they encounter.
- Knoppix can be difficult for novice users to install and configure, as it requires some technical knowledge.
- Updates to the version of Knoppix in use are only available from the official website, meaning that users may be running out-of-date versions of the software if they don’t regularly check for updates.
Knoppix is a free and open-source operating system that can be used without installation.
Knoppix: The Freedom of a Portable Linux Experience
Knoppix, the renowned free and open-source operating system, offers users a unique advantage: the ability to use it without installation. This remarkable feature sets Knoppix apart from traditional operating systems and opens up a world of possibilities for users who value flexibility and convenience.
The beauty of Knoppix lies in its “live” functionality. By simply booting from a CD or USB drive, users can experience the full power and capabilities of Knoppix without making any changes to their existing system. This means you can carry your own personal Linux environment with you wherever you go, allowing you to work, explore, or troubleshoot on any compatible computer.
This portable aspect of Knoppix has numerous advantages. Firstly, it enables users to test-drive Linux without committing to a full installation. Whether you’re new to Linux or curious about trying out different distributions, Knoppix provides a risk-free way to explore and familiarize yourself with this open-source ecosystem. You can experiment with various applications, tweak settings, and get a feel for the Linux environment before deciding if it’s the right fit for your needs.
Moreover, Knoppix’s portability makes it an invaluable tool for system administrators and IT professionals. In situations where access to critical data or troubleshooting is required on multiple machines, Knoppix’s live functionality allows for quick and efficient analysis without interfering with existing setups. It’s like having a Swiss Army knife in your pocket that can handle various tasks on different systems.
Another advantage of using Knoppix without installation is its compatibility with older or less powerful hardware. By running directly from external media, Knoppix bypasses the need for resource-intensive installations that may strain older machines. This makes it an excellent choice for reviving outdated systems or performing data recovery operations where preserving hardware resources is crucial.
Additionally, Knoppix’s “install-free” approach promotes privacy and security. Since no permanent changes are made to the host system, your personal data remains separate and secure. This is particularly useful when using public or shared computers, as you can rest assured that your sensitive information won’t be left behind or compromised.
Knoppix’s commitment to being free and open-source aligns with the principles of transparency, collaboration, and community-driven development. By providing a fully functional operating system without any licensing fees, Knoppix empowers users to embrace the spirit of open-source software and contribute to its growth.
In conclusion, Knoppix’s ability to be used without installation is a game-changer for those seeking freedom, versatility, and convenience in their computing experience. Whether you’re a curious user exploring Linux or a professional needing a portable tool for system management, Knoppix offers an exceptional solution. Embrace the power of this open-source gem and discover the endless possibilities it brings to your digital journey.
It can run on almost any computer, making it ideal for rescuing data from an old or damaged hard drive.
Knoppix: The Ultimate Data Rescuer for Old or Damaged Hard Drives
When it comes to rescuing data from old or damaged hard drives, Knoppix proves to be an invaluable tool. This remarkable Linux distribution has the exceptional ability to run on almost any computer, regardless of its age or condition. This makes Knoppix the go-to choice for those seeking to recover precious data from ailing storage devices.
One of the biggest challenges when dealing with old or damaged hard drives is finding a compatible operating system that can effectively access and retrieve the data stored within. This is where Knoppix shines. By simply booting up Knoppix from a CD or USB drive, users gain access to a powerful and versatile operating system that can breathe new life into their old or malfunctioning hardware.
Knoppix’s ability to run on a wide range of computers is made possible by its robust hardware detection capabilities. It excels at automatically recognizing and configuring various hardware components, ensuring seamless compatibility and optimal performance. Whether you’re dealing with an ancient desktop computer gathering dust in your attic or a laptop with a failing hard drive, Knoppix is there to help salvage your important files.
Data recovery using Knoppix is straightforward and user-friendly. Once booted into the Knoppix environment, users can navigate through its intuitive graphical interface and access a plethora of tools specifically designed for data rescue operations. Whether you need to copy files onto an external storage device, repair disk errors, or perform advanced partition recovery, Knoppix provides the necessary utilities to get the job done efficiently.
Moreover, Knoppix’s lightweight nature ensures that it runs smoothly even on older hardware configurations with limited resources. This means that you don’t need a high-end computer system to utilize its powerful data recovery capabilities. Simply pop in the Knoppix disc or plug in your USB drive, and you’re ready to embark on your data rescue mission.
The versatility of Knoppix extends beyond data recovery. It also serves as a valuable tool for assessing the health and performance of hard drives. With its comprehensive suite of diagnostic and troubleshooting tools, Knoppix allows users to identify and address potential issues that may be plaguing their storage devices. This proactive approach can help prevent data loss before it occurs, providing peace of mind to users who rely on their hard drives for critical information.
In conclusion, Knoppix’s ability to run on almost any computer makes it an indispensable asset for rescuing data from old or damaged hard drives. Its compatibility, user-friendliness, and range of powerful tools make it an ideal choice for anyone facing the daunting task of recovering important files from seemingly hopeless situations. Whether you’re a professional technician or a concerned individual trying to save cherished memories, Knoppix is the ultimate ally in your data rescue journey.
Knoppix: A Ready-to-Use Linux Solution with a Wealth of Applications
When it comes to Linux distributions, Knoppix stands out as a remarkable solution that offers users an extensive range of applications and tools right out of the box. This means that you can start using Knoppix immediately without the need to install additional software.
One of the key advantages of Knoppix is its comprehensive software package, which covers a wide spectrum of needs and interests. Whether you’re a student, professional, or hobbyist, Knoppix has something for everyone. From office productivity tools like word processors and spreadsheets to graphic design software and multimedia players, Knoppix has you covered.
With Knoppix, you can dive into educational resources with pre-installed applications for various subjects such as mathematics, physics, chemistry, and more. This makes it an excellent choice for students or anyone looking to expand their knowledge in a particular field.
For system administrators or IT professionals, Knoppix includes a plethora of powerful tools for system analysis, troubleshooting, and data recovery. Whether you need to diagnose hardware issues or recover lost files from a damaged system, these built-in tools can be invaluable in critical situations.
Furthermore, Knoppix supports various programming languages and development environments right from the start. This makes it an attractive option for software developers who want to quickly get started with coding without the hassle of installing additional development tools.
The convenience of having such a wide selection of applications readily available cannot be overstated. It saves time and effort that would otherwise be spent searching for and installing individual software packages. With Knoppix, you can hit the ground running and focus on your tasks or projects straight away.
Additionally, as an open-source distribution, Knoppix benefits from continuous community contributions and updates. This ensures that the included applications are regularly maintained and updated with new features or security patches.
In conclusion, Knoppix’s inclusion of a diverse range of applications and tools right from the start makes it an attractive choice for users who want a ready-to-use Linux solution. Whether you’re a student, professional, or enthusiast, Knoppix provides a comprehensive set of software packages to cater to your needs. By eliminating the need for additional installations, Knoppix offers convenience and efficiency, allowing you to get started with your work or exploration immediately. Give Knoppix a try and experience the power and versatility of this all-inclusive Linux distribution.
It provides good security features, such as encryption and secure booting options, making it suitable for sensitive tasks like online banking or storing confidential files.
Knoppix: A Secure Choice for Online Banking and Confidential File Storage
When it comes to sensitive tasks like online banking or storing confidential files, security is of utmost importance. This is where Knoppix, the pioneering live Linux distribution, truly shines. With its robust security features, including encryption and secure booting options, Knoppix provides users with a secure environment for handling sensitive information.
One of the standout features of Knoppix is its support for encryption. By utilizing powerful encryption algorithms, Knoppix ensures that your data remains secure and protected from unauthorized access. Whether you’re storing personal financial information or confidential business documents, you can have peace of mind knowing that your data is encrypted and safeguarded.
In addition to encryption, Knoppix offers secure booting options. Secure booting ensures that only trusted software components are loaded during the boot process, mitigating the risk of malware or other malicious software compromising your system. This feature adds an extra layer of protection against potential threats when performing critical tasks such as online banking.
Knoppix’s commitment to security extends beyond just software features. The distribution has a strong focus on providing regular updates and patches to address any security vulnerabilities that may arise. This proactive approach ensures that users are always protected with the latest security enhancements.
Furthermore, Knoppix’s open-source nature allows for thorough code reviews by security experts worldwide. This peer review process helps identify and rectify any potential vulnerabilities promptly, making Knoppix a reliable choice for those seeking a secure operating system.
By using Knoppix for online banking or storing confidential files, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to cyber threats such as identity theft or data breaches. Its robust security features create a fortified environment where your sensitive information remains safe from prying eyes.
It’s important to note that while Knoppix provides excellent security features, users must also practice good cybersecurity hygiene by keeping their systems up-to-date and using strong passwords. By combining Knoppix’s security measures with responsible user behavior, you can create a robust defence against potential security risks.
In conclusion, Knoppix’s focus on security makes it an ideal choice for tasks that involve handling sensitive information, such as online banking or storing confidential files. Its encryption and secure booting options, along with regular updates and open-source scrutiny, provide users with a secure environment for their most sensitive tasks. By choosing Knoppix, you can have confidence in the security of your data and enjoy peace of mind while conducting critical activities online.
It has excellent hardware detection capabilities, so it works well with older hardware components that may not be supported by newer operating systems.
Knoppix: The Perfect Solution for Older Hardware
In a world where technology advances at a rapid pace, it’s not uncommon for older hardware components to become incompatible with newer operating systems. This can be frustrating for users who still rely on their trusty machines but find themselves unable to upgrade due to compatibility issues. However, there is a shining light amidst this dilemma: Knoppix.
Knoppix, the pioneering live Linux distribution, boasts excellent hardware detection capabilities that make it an ideal choice for older hardware components. Unlike some modern operating systems that may overlook or struggle with identifying outdated devices, Knoppix excels at automatically recognizing and configuring them.
This means that even if you’re using a computer with aging hardware, Knoppix can breathe new life into it. You no longer need to worry about being left behind by the latest software updates or feeling restricted by compatibility limitations. With Knoppix, you can experience the power and versatility of Linux on your older machine without any hassle.
Thanks to its advanced hardware detection capabilities, Knoppix provides seamless support for various devices such as sound cards, graphics cards, network adapters, and more. It takes care of the intricate details behind the scenes so that you can focus on using your computer without any interruptions or frustrations caused by incompatible drivers.
Whether you’re repurposing an old computer for educational use, setting up a dedicated server with limited resources, or simply want to extend the lifespan of your beloved machine, Knoppix is here to help. Its ability to work well with older hardware components opens up new possibilities and ensures that you can continue using your trusted devices without compromise.
Moreover, Knoppix’s commitment to user-friendliness ensures that even those who are less experienced in navigating Linux distributions can benefit from its excellent hardware detection capabilities. The intuitive graphical user interface (GUI) provides easy access to all essential functions and applications while maintaining familiarity for users transitioning from other operating systems.
In conclusion, Knoppix’s outstanding hardware detection capabilities make it a standout choice for users with older hardware components. It eliminates the frustration of compatibility issues and allows you to make the most out of your trusted machines. With Knoppix, you can enjoy the power, security, and reliability of Linux without worrying about whether your hardware is up to the task.
So if you have an older computer that you thought was destined for retirement, think again. Give Knoppix a try and experience firsthand how this exceptional live Linux distribution can transform your old hardware into a fully functional and reliable system once again.
The graphical user interface is easy to use and navigate, even for beginners who are unfamiliar with Linux-based systems .
Knoppix: A Beginner-Friendly Linux Distribution with an Intuitive Graphical User Interface
For those new to the world of Linux-based operating systems, navigating through unfamiliar territory can often feel daunting. However, Knoppix stands out as an excellent choice for beginners, thanks to its user-friendly graphical user interface (GUI) that simplifies the Linux experience.
One of the standout features of Knoppix is its intuitive GUI, which provides a familiar and easy-to-navigate environment even for those who are completely new to Linux. With its well-designed interface, users can quickly find their way around and access various applications and system settings without feeling overwhelmed.
The developers behind Knoppix have put considerable effort into creating a GUI that resembles the look and feel of other popular operating systems like Windows. This design choice makes it easier for beginners to transition from their familiar computing environments to the world of Linux without experiencing a steep learning curve.
With Knoppix’s GUI, users can effortlessly browse through files and folders, launch applications with a few clicks, and customize their desktop according to their preferences. The simplicity and intuitiveness of the interface make it an ideal choice for individuals who may not have extensive technical knowledge but still want to explore the power and flexibility that Linux offers.
In addition to its user-friendly design, Knoppix also provides comprehensive documentation and online support resources. These resources are specifically tailored to assist beginners in getting started with the distribution. Whether you need guidance on installing software or understanding core concepts of Linux, you’ll find ample assistance readily available.
Knoppix’s commitment to providing a beginner-friendly experience doesn’t compromise its functionality or versatility. Behind its user-friendly GUI lies a robust set of tools and applications that cater to various needs. From productivity software like office suites and web browsers to multimedia tools for entertainment purposes, Knoppix offers a wide range of applications right at your fingertips.
Moreover, Knoppix’s focus on hardware compatibility ensures that most devices are automatically detected and configured, eliminating the need for manual driver installations. This feature is particularly beneficial for beginners who may not have the technical expertise to troubleshoot hardware-related issues.
In conclusion, Knoppix’s user-friendly graphical user interface makes it an excellent choice for beginners venturing into the world of Linux. Its intuitive design, reminiscent of popular operating systems, allows users to quickly adapt and navigate through the system with ease. With comprehensive documentation and online support, Knoppix provides a welcoming environment for newcomers to learn and explore Linux-based systems.
If you’re a beginner looking to dip your toes into Linux or simply seeking a distribution that prioritizes ease of use without compromising functionality, Knoppix is definitely worth considering. Give it a try and embark on your Linux journey with confidence.
Knoppix comes with plenty of documentation and tutorials which makes learning how to use the OS easier than ever before!
Knoppix: Empowering Users with Extensive Documentation and Tutorials
When it comes to learning a new operating system, having access to comprehensive documentation and tutorials can make all the difference. This is where Knoppix truly shines. As a leading Linux distribution, Knoppix has gone above and beyond to provide users with an abundance of resources that make learning how to use the OS easier than ever before.
One of the standout features of Knoppix is its extensive documentation. Whether you’re a complete beginner or an experienced user, the documentation covers everything you need to know about using Knoppix effectively. From installation instructions to advanced configuration options, each aspect of the operating system is explained in detail, ensuring that users have all the information they need at their fingertips.
But that’s not all – Knoppix goes even further by offering a wide range of tutorials. These step-by-step guides walk users through various tasks and functionalities, making it easy for anyone to grasp the intricacies of the OS. Whether you want to learn how to customize your desktop environment, set up networking options, or explore advanced system administration techniques, there’s a tutorial available for almost every aspect of Knoppix.
The availability of such extensive documentation and tutorials is invaluable for both newcomers and experienced Linux enthusiasts. Beginners can rely on these resources as a starting point for their journey into the world of Linux. They can follow along with clear instructions and gain confidence in using Knoppix without feeling overwhelmed by technical jargon.
For experienced users, the documentation serves as a handy reference guide when exploring new features or troubleshooting issues. It saves time by providing quick answers to common questions and acts as a reliable resource for expanding their knowledge and skills within the Knoppix ecosystem.
Furthermore, this commitment to providing comprehensive resources demonstrates Knoppix’s dedication towards fostering an inclusive community. By making learning accessible and enjoyable for everyone, regardless of their technical background or experience level, Knoppix encourages users to explore the vast possibilities of Linux and contribute to the open-source community.
In conclusion, Knoppix’s wealth of documentation and tutorials sets it apart as a user-friendly Linux distribution. Its commitment to empowering users by providing comprehensive resources ensures that anyone can learn and harness the full potential of this powerful operating system. Whether you’re a beginner taking your first steps into the world of Linux or an experienced user looking to expand your knowledge, Knoppix’s extensive documentation and tutorials are there to support you every step of the way.
Knoppix is not compatible with all hardware, which may limit its usefulness.
Knoppix: A Powerful Linux Distribution with Hardware Compatibility Considerations
While Knoppix has established itself as a leading live Linux distribution, it’s important to acknowledge that its compatibility with all hardware configurations may be limited. This aspect can potentially impact its usefulness for certain users.
One of the challenges faced by any operating system is ensuring compatibility with a wide range of hardware components. Knoppix, like other Linux distributions, relies on community-driven efforts to provide drivers and support for various devices. However, due to the vast array of hardware available in the market, it is inevitable that some configurations may not be fully supported.
For users with less common or newer hardware, there is a possibility that Knoppix may not recognize or function optimally with certain devices. This can present obstacles for those who heavily rely on specific hardware components or require seamless integration for their work or projects.
It’s worth noting that the Knoppix development team continuously works to improve hardware compatibility through regular updates and new releases. They strive to address known issues and expand support for a wider range of devices. However, it’s important for users to be aware of this limitation and consider their specific hardware requirements before relying solely on Knoppix as their primary operating system.
Despite these compatibility considerations, many users still find immense value in Knoppix’s versatility and functionality. It remains an excellent choice for data recovery purposes, system administration tasks, educational use, or simply exploring the world of Linux without making any changes to an existing system.
Moreover, even if Knoppix doesn’t fully support all hardware configurations out-of-the-box, there are often workarounds available within the Linux community. Dedicated enthusiasts have created additional drivers or guides to help users overcome compatibility issues and make the most out of their Knoppix experience.
In conclusion, while Knoppix offers numerous advantages as a live Linux distribution, its compatibility limitations with certain hardware configurations should be taken into account. Users with unique or specific hardware requirements may need to explore alternative Linux distributions that better suit their needs. However, for those seeking a portable and versatile operating system with a wide range of applications, Knoppix remains a valuable choice, supported by a dedicated community that strives to enhance its compatibility over time.
Knoppix does not come with any technical support, so users must find their own solutions to any problems they encounter.
Knoppix: A Self-Sufficient Linux Distribution
While Knoppix has gained recognition for its pioneering live Linux distribution and user-friendly design, it is important to note one potential drawback: the absence of official technical support. Unlike some other Linux distributions that offer dedicated support channels, Knoppix leaves users to find their own solutions when encountering problems.
For many users, this may not be a significant issue. Knoppix has a strong online community of knowledgeable enthusiasts who are often willing to lend a helping hand. Various forums, discussion boards, and online resources are available where users can seek advice and find solutions from fellow Knoppix users.
Furthermore, the comprehensive documentation provided by Knoppix can be immensely helpful in troubleshooting common issues. The documentation covers topics ranging from installation guides to system administration tasks, providing step-by-step instructions and explanations.
However, it is worth noting that relying solely on community-driven support may present challenges for users facing complex or unique problems. In such cases, finding specific answers or receiving timely assistance might require more effort and research compared to distributions with dedicated technical support teams.
To mitigate this limitation, it is advisable for Knoppix users to explore external resources such as general Linux forums or seek assistance from experienced Linux professionals who have broader knowledge across different distributions. These alternative avenues can provide additional insights and guidance when tackling intricate issues that go beyond the scope of the Knoppix community.
Despite this con, it is important to recognize that the lack of official technical support does not diminish the value of Knoppix as a powerful and versatile Linux distribution. Its user-friendly interface, extensive software package selection, and hardware detection capabilities continue to make it a popular choice among both beginners and experienced Linux enthusiasts.
In conclusion, while Knoppix may not provide direct technical support like some other distributions do, its vibrant community and wealth of online resources offer ample opportunities for users to find solutions independently. By tapping into these resources and exploring external avenues, Knoppix users can navigate any challenges they encounter and continue to enjoy the benefits of this innovative live Linux distribution.
Navigating the Technical Challenges of Knoppix Installation and Configuration
While Knoppix has gained recognition as a pioneering live Linux distribution, it is important to acknowledge that it may present some challenges for novice users when it comes to installation and configuration. Due to its technical nature, Knoppix requires a certain level of knowledge and expertise to set up successfully.
For those unfamiliar with Linux or operating systems in general, the installation process of Knoppix can be daunting. Unlike traditional operating systems that come with streamlined installation wizards, Knoppix requires users to manually configure certain settings during the installation process. This can include partitioning disks, selecting boot options, and setting up network connections.
Additionally, configuring hardware components can be another hurdle for novice users. While Knoppix is known for its excellent hardware detection capabilities, there may still be instances where additional configuration is required. This can involve setting up drivers for specific hardware devices or troubleshooting compatibility issues.
Understanding the intricacies of configuring software applications is another challenge that novice users may encounter with Knoppix. While the distribution comes bundled with a wide range of software options, knowing how to install additional applications or customize existing ones may require some technical knowledge.
However, it’s important to note that these challenges are not insurmountable. With a willingness to learn and some guidance, even novice users can overcome these hurdles and fully enjoy the benefits of Knoppix.
Fortunately, there are many online resources available that provide step-by-step tutorials and support forums dedicated to helping users navigate through the installation and configuration processes. These resources offer valuable insights into common issues faced by beginners and provide solutions tailored to their needs.
Furthermore, community engagement plays a significant role in assisting novice users with their journey into using Knoppix. By actively participating in forums or seeking guidance from experienced community members, beginners can tap into a wealth of knowledge and receive personalized assistance when encountering difficulties during installation or configuration.
While Knoppix may present some technical challenges for novice users, it is important to view these hurdles as opportunities for growth and learning. The open-source community surrounding Knoppix is known for its inclusivity and willingness to help newcomers. With determination, patience, and support from the community, even those with limited technical knowledge can successfully install and configure Knoppix.
In conclusion, while Knoppix may require some technical expertise to install and configure, it should not discourage novice users from exploring this powerful Linux distribution. By leveraging available resources and engaging with the supportive community, beginners can overcome these challenges and embark on a rewarding journey into the world of Knoppix.
Updates to the version of Knoppix in use are only available from the official website, meaning that users may be running out-of-date versions of the software if they don’t regularly check for updates.
The Importance of Regular Updates: A Consideration with Knoppix
Knoppix, the pioneering live Linux distribution, has garnered a significant following for its versatility and user-friendly design. However, like any software, it is not without its drawbacks. One notable con of using Knoppix is the limited availability of updates outside of the official website. This means that users may inadvertently run outdated versions of the software if they fail to regularly check for updates.
Regular updates are crucial for any operating system as they provide essential bug fixes, security patches, and feature enhancements. By keeping your software up-to-date, you ensure that you have access to the latest improvements and safeguards against potential vulnerabilities.
With Knoppix, updates are primarily distributed through its official website. While this centralized approach ensures that users can obtain updates directly from the source, it also places a responsibility on users to actively monitor and install these updates themselves. Failure to do so may result in running an outdated version of Knoppix, potentially exposing your system to security risks or missing out on new features.
To address this con effectively, it is recommended that Knoppix users establish a routine for checking for updates on the official website. Regularly visiting the site or subscribing to relevant mailing lists or RSS feeds can help ensure that you stay informed about new releases and important updates.
Additionally, exploring community-driven forums and discussion boards related to Knoppix can provide valuable insights into any unofficial patches or workarounds that may be available from other users. While these alternatives may not offer the same level of assurance as official updates, they can serve as temporary solutions until official patches become available.
It is important to note that this con should not overshadow the many benefits offered by Knoppix. Its innovative live Linux distribution model and user-friendly interface continue to make it a popular choice among both beginners and experienced Linux enthusiasts. However, staying vigilant about updating your Knoppix installation will help ensure that you have the most secure and feature-rich experience possible.
In conclusion, while Knoppix’s limited availability of updates outside of the official website may be seen as a con, it can be effectively managed by establishing a regular update-checking routine and staying engaged with the Knoppix community. By actively monitoring for updates, users can mitigate any potential risks associated with running outdated versions of the software and continue to enjoy all the benefits that Knoppix has to offer.